As we discussed last week, King’s is currently reviewing the methods and guidelines that exist for fundraising, research grants, procurement and investments. Aligning procedures with ethical values matters because it signals an active commitment to shifting our economy towards a low-carbon trajectory.
Building a more sustainable institution requires more than rewriting existing policy, however. At a practical level, our most significant environmental impact stems from keeping the lights on across our sites. With 27,600 registered students, 6,600 staff members, five London campuses and more than ten halls of residence, King’s is a prodigious consumer of energy. Reducing our carbon footprint through investments in energy efficiency and switching to alternative forms of energy therefore represents an area of significant potential impact.
King’s College London has committed to a reduction of 43% in carbon emissions by 2019/2020 against a 2005/06 baseline. This effort has been targeted at emissions arising from the use of oil, gas and electricity in daily operations. As outlined in the 2011 Carbon Management Plan, King’s low carbon vision is to reduce carbon emissions through the application of energy efficiency methods and the use of low carbon technologies.
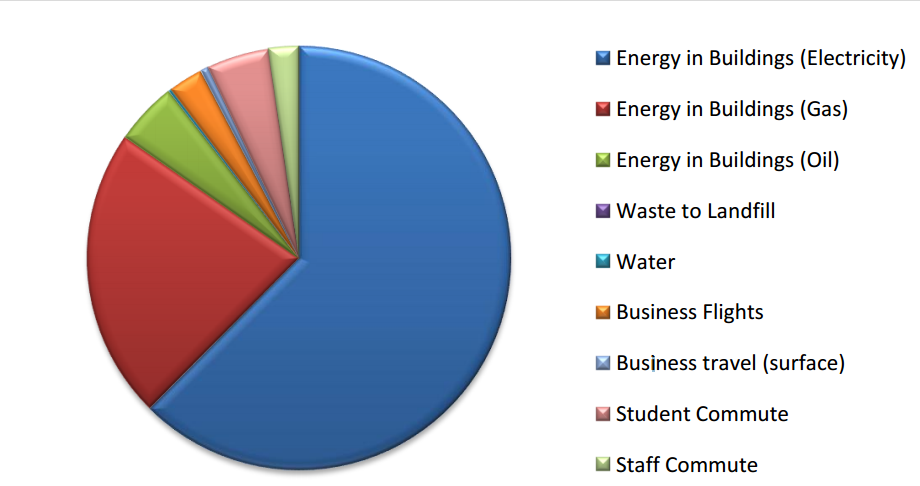
CO2 emissions 2008-2009: Energy use in buildings comprises the vast majority of the total footprint
Investing in smarter, greener and less energy-intensive systems is already bringing economic and environmental dividends. Since 2005/06, the implementation of the Carbon Management Plan has led to annual savings of approximately £3.6m. In 2014/2015 alone, investments in energy efficiency projects led to reductions in excess of 688tCO2e.
Yet, as the number of King’s students and staff continues to grow and as the university expands to new sites, there is a need to scale investments in carbon reduction projects to achieve the 43% reduction target by 2019/2020. Jon Wibberley, Karen Shaw and the wider Sustainability Team are continuously working towards identifying the most promising areas for investment in energy savings.
Over the past year, this effort has centred on upgrading heating and lighting in a number of King’s Residences. Undoubtedly, the most eye-catching of these carbon reduction projects has been the installation of solar panels on the roof of the Great Dover Street Apartments (GDSA). The panels were installed on Blocks 1-10 of GDSA in the spring semester of 2016 and are now fully operational.
With a net capacity of 84.97kW and an estimated annual electricity generation of 71,510 kWh, the panels are expected to result in annual onsite savings of £9,140. These savings are projected to increase by approximately £1000 p.a. going forward to 2025. At an installation cost of £119,635, this represents excellent value for money.
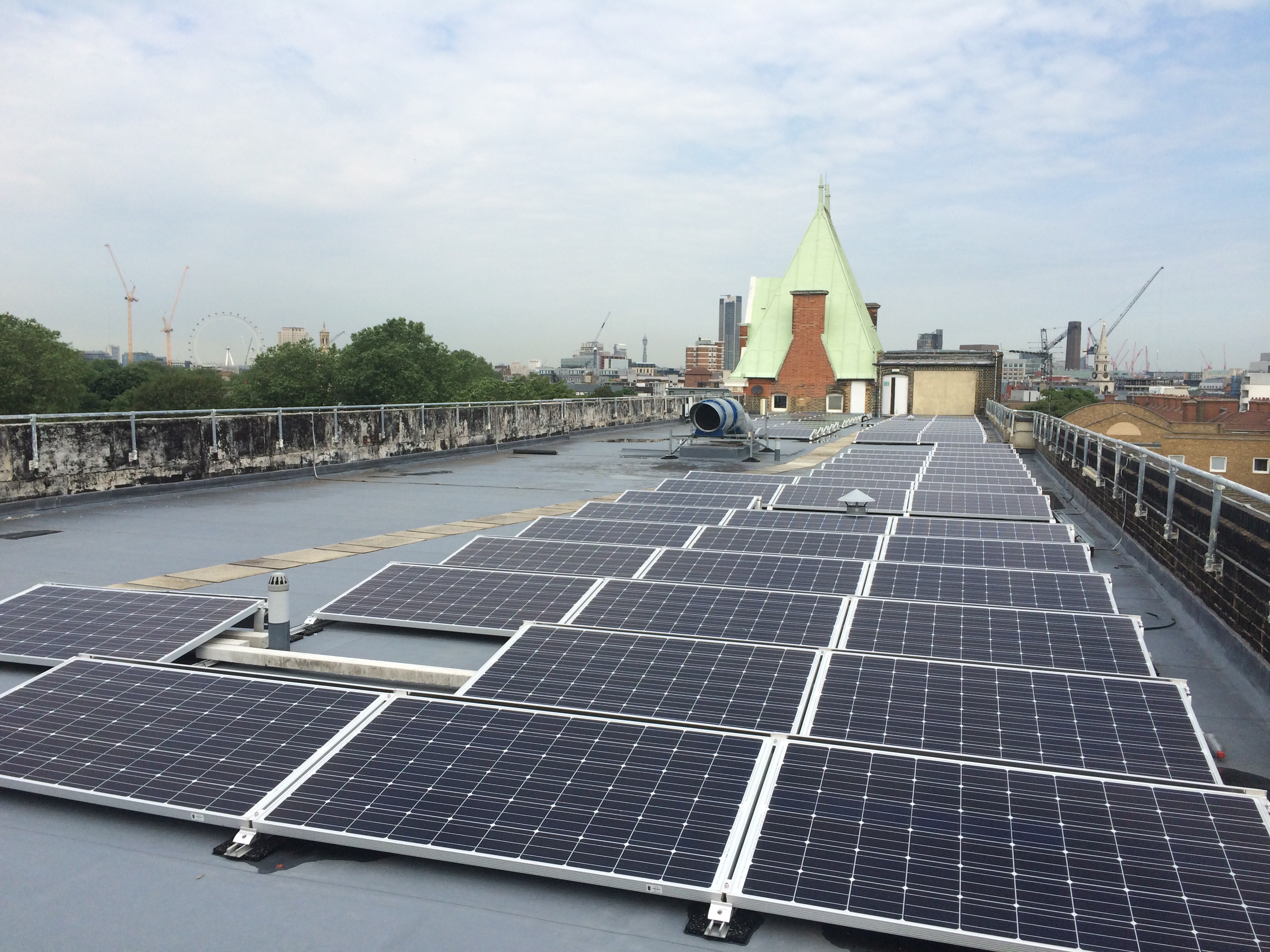

Solar panels on the roof of GDSA
The solar panel installation at GDSA is not solely the product of long-sighted thinking by the King’s Energy team, however. Students were involved in initial conversations held between KCLSU and KCL to jointly fund the GDSA solar panels. In the end the UK government’s decision to reduce the feed-in tariffs from January 1st 2016 meant that there was not enough time to finalise the project. Nevertheless, Energy Management Coordinator Karen Shaw credits the broad student support for renewable energy and energy efficiency initiatives as important in “building momentum for future projects”.
This support is evident through the actions taken in the student council. In 2014/2015 two key motions were adopted: one formulated an Ethical Investment Policy while the other encouraged KCLSU to explore alternative ethical banking providers. The outcome of this combined effort was that KCLSU moved a third of its reserves to an account with the ethical investment bank Triodos and replaced Natwest with MetroBank as its commercial banking provider.
Student involvement is not only important in helping carbon reduction projects get off the ground, but also in ensuring they are successful once they lift off. In addition to the solar panels, the spring semester saw several other upgrades at GDSA: personal fridges were replaced by larger communal fridges in the kitchens, LED lights and presence detectors were installed in kitchens and hallways and a more efficient heating system will be installed. These changes are part of a five year refurbishment project taking place at both Great Dover Street and Stamford Street.
A number of other major projects which have been completed successfully are worth mentioning: solar PV and Combined Heat & Power (CHP) is contributing to substantial energy savings at Champion Hill; Ground Source Cooling has been installed at the at the Wohl; Ground Source Heat Pumps are in operation at Cicely Saunders and both Cicely Saunders and Honour Oak Park use solar thermal energy to heat water.

Honour Oak Park
Many more projects are in the pipeline over the next couple of years as part of a broader strategy to “design out” energy use from daily operations.
Yet, technological solutions can only go so far. Achieving real energy savings requires the participation of students. And here the good news is that lots of students are very conscious of the need to save energy. This past academic year, students in Stamford Street Apartments, Great Dover Street Apartments, Wolfson House and Champion Hill used 4.3% less energy compared to the 2014/15 academic year. Students play a role both in conserving energy and in identifying areas of energy wastage.
Going forward we hope to build on these achievements and lower our impact further. Students will remain central to this ambition being realised.
As always if you have comments, queries or suggestions do not hesitate to get in touch:
tobias.1.udsholt@kcl.ac.uk / sustainability@kcl.ac.uk
Follow us on twitter @KCLSustainable
Tobias Udsholt, Sustainability Projects Assistant
















 itself from the fossil fuel industries. For those who have not followed the progress of the campaign, it really kicked off in October with the submission of a 1200 signature petition to the university administration. While that number has since increased to over 1400, the university finally declined the divestment option formally in mid-February. However, much to King’s credit, the Principal’s Debate went ahead as scheduled, and it made for a most lively and engaging evening, and further demonstrated the scope of the passionate support for divestment at King’s.
itself from the fossil fuel industries. For those who have not followed the progress of the campaign, it really kicked off in October with the submission of a 1200 signature petition to the university administration. While that number has since increased to over 1400, the university finally declined the divestment option formally in mid-February. However, much to King’s credit, the Principal’s Debate went ahead as scheduled, and it made for a most lively and engaging evening, and further demonstrated the scope of the passionate support for divestment at King’s. known carbon reserves will be left in the ground. Given that fossil fuel companies are valued largely on the reserves they hold, these so-called ‘stranded assets’ would rapidly sink such companies and lead to a crisis similar to that when the US housing bubble burst in 2008, only far worse. That bubble was worth a staggering $2.8 trillion. The value of the carbon bubble? An unfathomable $28 trillion. Campanale explained carefully the financial folly in continuing to invest in companies whose future projects are all but guaranteed to lose money, providing a sound financial case for divestment.
known carbon reserves will be left in the ground. Given that fossil fuel companies are valued largely on the reserves they hold, these so-called ‘stranded assets’ would rapidly sink such companies and lead to a crisis similar to that when the US housing bubble burst in 2008, only far worse. That bubble was worth a staggering $2.8 trillion. The value of the carbon bubble? An unfathomable $28 trillion. Campanale explained carefully the financial folly in continuing to invest in companies whose future projects are all but guaranteed to lose money, providing a sound financial case for divestment.



