This week’s guest blog comes fifth in a series of blogs on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) courtesy of Onna Malou van den Broek, second year doctorate student at King’s in the European & International Studies Department. Onna’s doctorate project titled: ‘The Political Payoff of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): CSR as a Determinant for Lobbying Success’, which looks at the relationship between corporate sustainability and lobbying, holding a special focus on the SDGs.
On International Women’s Day the Global Institute for Women’s Leadership at King’s College London released a study on attitudes toward gender equality around the world (1). Results showed that 52 percent of the respondents believe that there are more advantages to be a man than a woman. Julia Gillard, former Prime Minister of Australia, reflected: “people rightly believe gender equality has not gone far enough. While the issues we prioritise may be different country by country, there is a real consensus that men must play their part if we are to achieve true parity between the sexes.”
The targets: Gender equality and the position of women
Even though the term gender equality suggests different forms of gender identification, SDG5 concentrates primarily on the position of women and girls in society (2). The targets focus on private and public domains as well as economical, social and political positions. Foremost, all gender-based discrimination and violence must be eliminated. Furthermore, unpaid labour, such as domestic responsibilities, must be acknowledged to ensure social security; women must have access to contraception; and policy around gender equality should be enforced. Additionally, women must have the same economic property rights and the same opportunities for leadership positions as men.
The current situation: Numbers versus reality
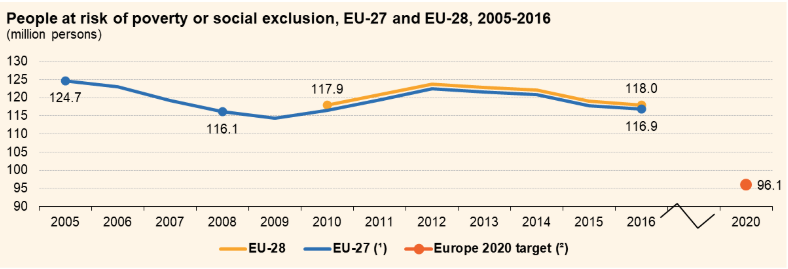
Globally, there has been some progression in certain areas of gender equality. For example, the participation of women in parliament increased from 13 percent in 2000 to 23 percent in 2017. Furthermore, the number of child marriages slightly decreased, however, 650 million girls and women today were still married in childhood. Progress has been slow; for example, there has been a 1% change in the percentage of senior management roles held by women globally in the last 10 years. In some sectors progress has even been reversed; the percentage of female ICT specialists in the EU has decreased by 6%. Note that numbers only tell part of the story. A lot of gender-based violence and discrimination remains hidden due to shame, taboos or the lack of data availability.
Lacking leadership from the West: The case of the Netherlands
Gender inequality is something that is apparent in both poor and rich countries. My birth country, the Netherlands, for example, dropped from the 16th to 32nd place in the world rankings. Countries such as Moldavia and Mozambique have catch up. This is largely due to the weak political and economic position of women as well as the growing inequality in income and health. To illustrate, there is a gender pay gap of 16 percent, female parliamentarians dropped to 37 per cent and only 26 per cent of management positions is filled by women. A national hero is our former minister Lilianne Ploumen. With her organization She Decides, she fights for sexual and reproductive rights, and even filled in the gap of anticonception supply caused by the Global Gag Rule of US president Trump.
The new feminism: I am a nasty woman
The good news is that the attention for women emancipation is on the rise. In response to comments by Trump such as “grab them by the pussy” and “those are just nasty women”, multiple protests have been organized. For example, the Women’s March in Washington during which actress Alshley Judd performed a poem of teenager Nina Donovan titled “nasty woman” (3). Another example is the hashtag #MeToo which sought to increase awareness for sexual intimidation after several scandals of sexual coercion in Hollywood. Global governance organizations have introduced informal projects as well, to illustrate European Union and the United Nations have founded the Spotlight Initiative to combat violence towards women and girls (4).
Abby Wambach and the Wolfpack
A book on this topic to watch is from Abby Wambach, a two-time Olympic gold medalist and FIFA World Cup champion (5). Based on her experience as a top athlete, she argues that: “it’s time for women to know the power of their wolves and the strength of their pack”. If we keep on playing by the old rules of leadership, we will never change the game. In the book Abby creates a new set of rules to help women unleash their individual power as well as to unite with other women and create a new world together. To do this, we need to make failure fuel, lead from wherever you are, champion other women and demand what you (and others) deserve!
Step up: Be a champion for gender equality.
Because gender inequality is often socially constructed, the most important thing you can do is to step up for your rights and/or the women in your direct environment. It is not ok if a female colleague is payed less than her man colleague, it is not ok if a female colleague is never nominated for promotion nor is it ok if colleagues make jokes about women in the kitchen or sexual intimidation. Furthermore, there are various initiatives you can support. For example, HeForShe has several projects about online violence towards women and breaking through taboos on sexual health (6). Remember, gender equality is EVERYONE’s business.
Notes:
- You can read the research here: https://www.kcl.ac.uk/news/news-article?id=d101993b-2363-45c7-bf59-047ee986a9ab
- To read more about the targets, indicators and the state-of-art, please go to: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/gender-equality/
- The poem is definitely worth a read: https://www.scarymommy.com/ashley-judd-speech-womens-march/
- Read more about the spotlight initiative: https://www.un.org/en/spotlight-initiative/index.shtml
- Visit Abby’s personal website to read more about her book: http://abbywambach.com/books/wolfpack/
- Learn how you can be the change: https://www.heforshe.org/en