This guest blog comes courtesy of Chloe Foster, third year undergraduate student in the War Studies Department and Student Assistant to the Social Science Public Policy (SSPP) Sustainability Champions.

Climate change is set to impact our lives in a variety of ways, but one particular global system is set to experience drastic consequences. Our current food system is not secure enough to sustain the challenges of the future because of increased extreme weather conditions, decreased biodiversity and increased emissions. A model developed by Anglia Ruskin University found that if ‘do-nothing’ trends continue, by 2040, the global food supply will be facing food epidemics and mass insecurity. This prediction suggests that SDG 2, Zero Hunger is not as achievable as previously thought. Whilst the aforementioned future challenges are not the whole list, this blog post will explore these main areas impacting global food security.
Extreme Weather Conditions
As the Earth’s temperature has risen, the frequency of extreme weather events has increased. Among others, these events include heat waves, drought and flooding. In autumn of last year, Nigeria faced huge flooding which directly impacted on food security and created shortages of rice. The USA has also experienced extreme weather recently; Hurricanes Harvey and Irma caused mass devastation of civilian, commercial and agricultural property. Whilst these natural disasters often pose an immediate threat to human safety, they also threaten crop growth and yields. Climate change is set to reduce harvest yields by 11% on average globally by 2050 and compound the already problematic state of food security. Research conducted by Oxfam found that weather-related shocks have the potential to cause huge spikes in food prices and the average price of staple foods, like cereals, could more than double in the next 20 years.
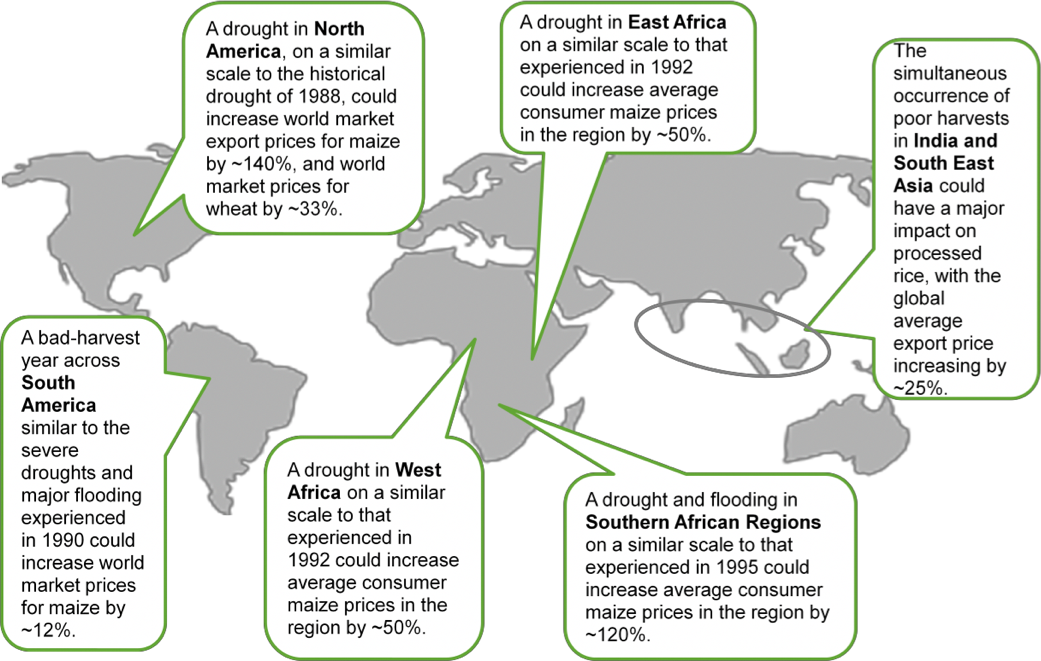
(Source – Oxfam Issue Briefing, GROWING DISRUPTION, Climate change, food, and the fight against hunger, September 2013)
Upcoming event – A new 30-year record of global wildfire activity from the AVHRR GAC archive
22 March 2019, 17:15 to 18:15 (Bush House North East Wing, Strand Campus, London)
Decreasing Biodiversity
The Food and Agriculture Organisation published a report in February of this year, detailing the increasing loss of biodiversity and its vital role in our food systems. The microorganisms (such as insects, birds and fungi), animals (like hedgehogs) and plants act as fertilisers, pollinators and purifiers of the environment, ensuring the healthy growth of the world around us. However, changes in the environment have led to biodiversity loss and the increased risk of increased food insecurity. Almost 1/3 of fish stocks are over fished, around 26% of breeds of livestock are at risk of extinction and 24% of wild food species numbers are decreasing. However, biodiversity-friendly practices are being increasingly using in agriculture and conservation efforts are increasing across the globe. Whilst these efforts will reduce the speed of biodiversity loss, sustainable frameworks should be used more by governments to formalise these attempts. King’s is promoting biodiversity across its campuses. At Guy’s, there are insect houses and bird boxes, at the Strand campus events are often held on the subject and the installation of green walls and greener spaces are being looked into.
Upcoming event – Biodiversity conservation in the 21st century: Lessons from northeastern China
15 March 2019, 17:15 to 18:15 (Bush House North East Wing, Strand Campus, London)
Emissions
The agricultural sector contributes to global warming in many ways. Research by Friends of the Earth, an environmental NGO, concluded that agriculture (including deforestation needed to create farmland) is responsible for roughly a 1/3 of global greenhouse gasses. The production of meat and dairy produce 51% of worldwide global emissions alone and their consumption is set to double between 2001 to 2050. These shocking figures highlight how our diets have a direct relationship to our carbon footprint and our responsibilities as consumers to make more eco-friendly choices. Changing our diets to be more plant-based and seasonal is an easy and effective way to live more sustainably. The Fetch-Ur-Veg scheme at King’s is a great way to get involved with this. With the scheme you get a weekly bag of amazing seasonally and locally produced fruit and vegetables, delivered straight to the Maughan library! If you’re stuck for recipes, take inspiration from their Facebook page!

Concluding Thoughts
Whilst these issues have solutions based in systemic change, there is still power in the individual. As such, I would still promote small changes that can be made to everyday life to reduce your impact on the earth. Eating a more plant-based diet, using more emission-friendly travel and being kind to the world around, individuals can also have a big impact, locally and in the bigger picture. Using http://www.footprintcalculator.org to work out your ecological footprint is a good place to start your sustainability journey!








 With more and more companies now offering Fairtrade chocolate, Easter is the perfect opportunity to support the scheme. The
With more and more companies now offering Fairtrade chocolate, Easter is the perfect opportunity to support the scheme. The  ood, Easter can also be a great time to enjoy the (hopefully) warm weather! With the stressful exam period coming up, making use of green spaces can help clear your mind – even if you don’t have time for extended walks, you could move your workspace outside for a few days. There are plenty of green spaces around London (e.g. Richmond Park, Southwark Park, Primrose Hill, Hampstead Heath etc.), and if you want to get your hands dirty, you can try out some
ood, Easter can also be a great time to enjoy the (hopefully) warm weather! With the stressful exam period coming up, making use of green spaces can help clear your mind – even if you don’t have time for extended walks, you could move your workspace outside for a few days. There are plenty of green spaces around London (e.g. Richmond Park, Southwark Park, Primrose Hill, Hampstead Heath etc.), and if you want to get your hands dirty, you can try out some  The conference started with a keynote speech by Amanda MacKenzie OBE, who highlighted the importance of getting everyone involved. When the SDGs were unveiled, she ran a campaign to get word about them out there. One of the key messages of this was the importance of using simple language everyone understands. This is why she refers to the goals as Global Goals rather than SDGs, claiming the term SDGs “sounds like something you would see your doctor about”. By calling them the Global Goals and making them accessible, we should be able to take millions of small, simple actions, together adding up to significant change.
The conference started with a keynote speech by Amanda MacKenzie OBE, who highlighted the importance of getting everyone involved. When the SDGs were unveiled, she ran a campaign to get word about them out there. One of the key messages of this was the importance of using simple language everyone understands. This is why she refers to the goals as Global Goals rather than SDGs, claiming the term SDGs “sounds like something you would see your doctor about”. By calling them the Global Goals and making them accessible, we should be able to take millions of small, simple actions, together adding up to significant change.

