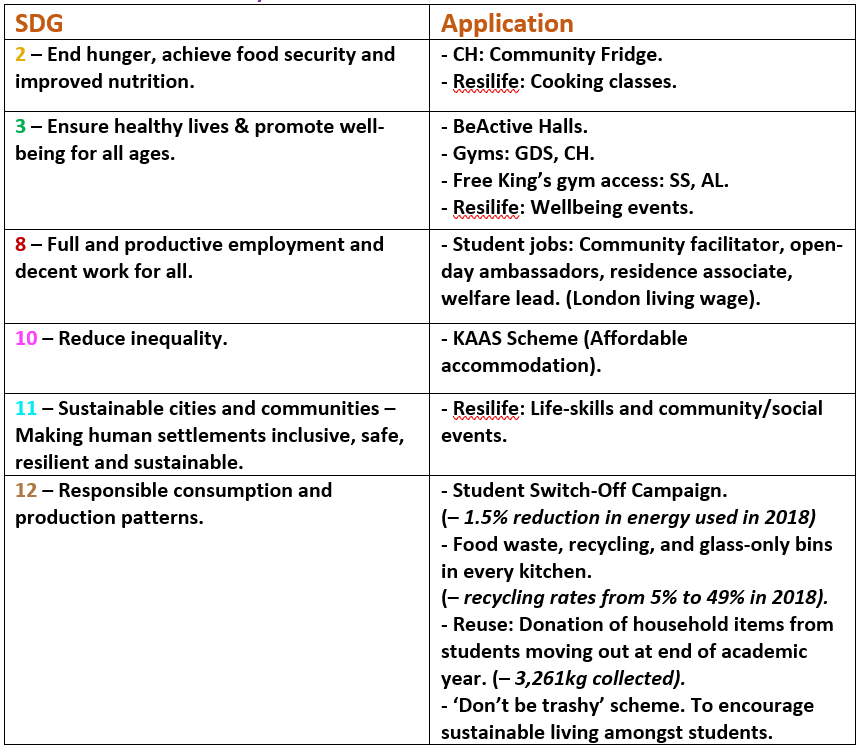
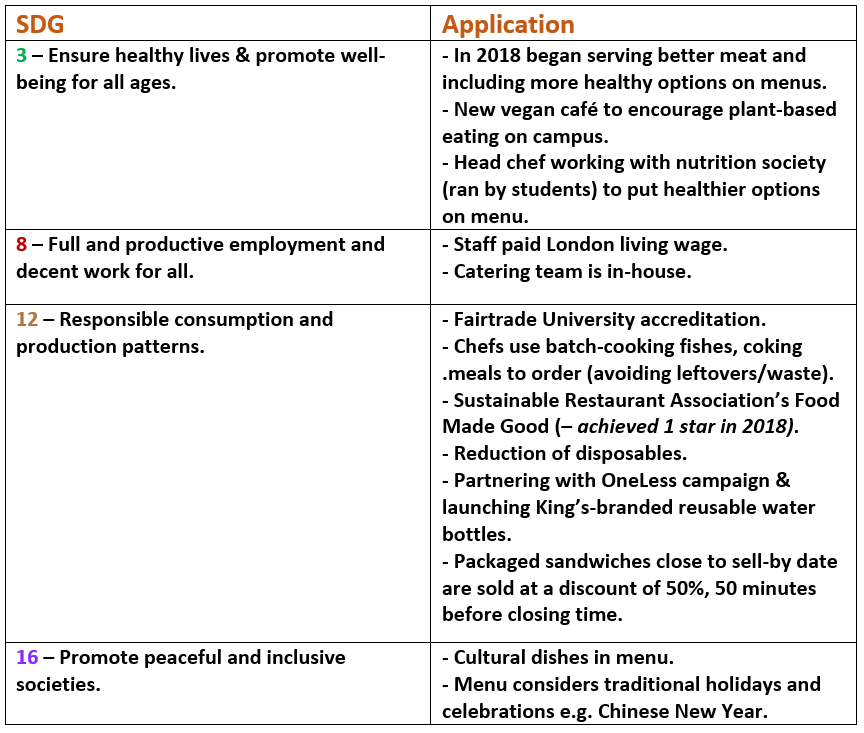
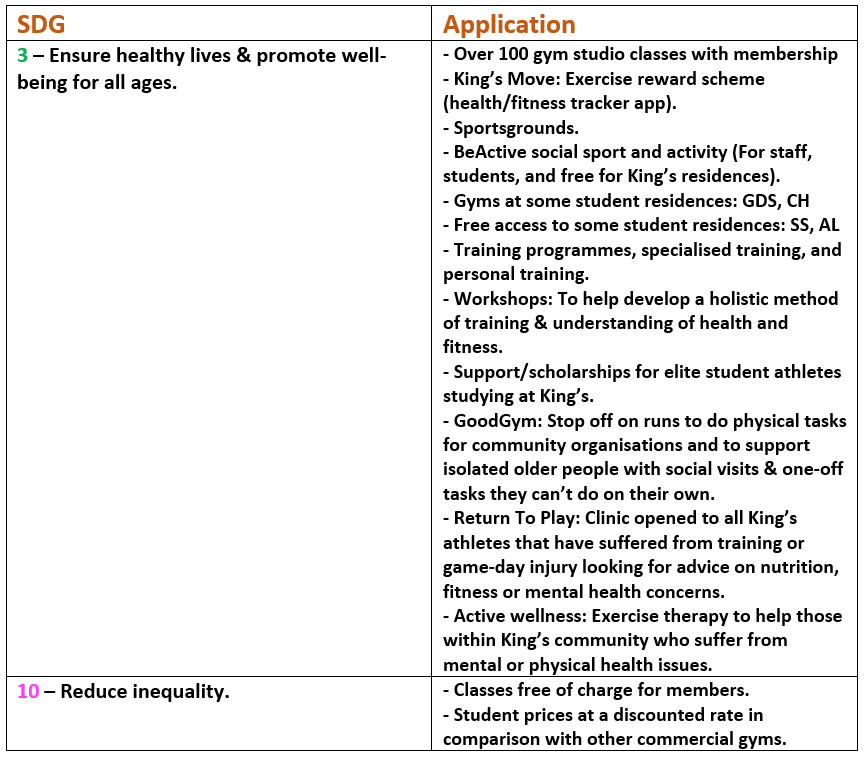
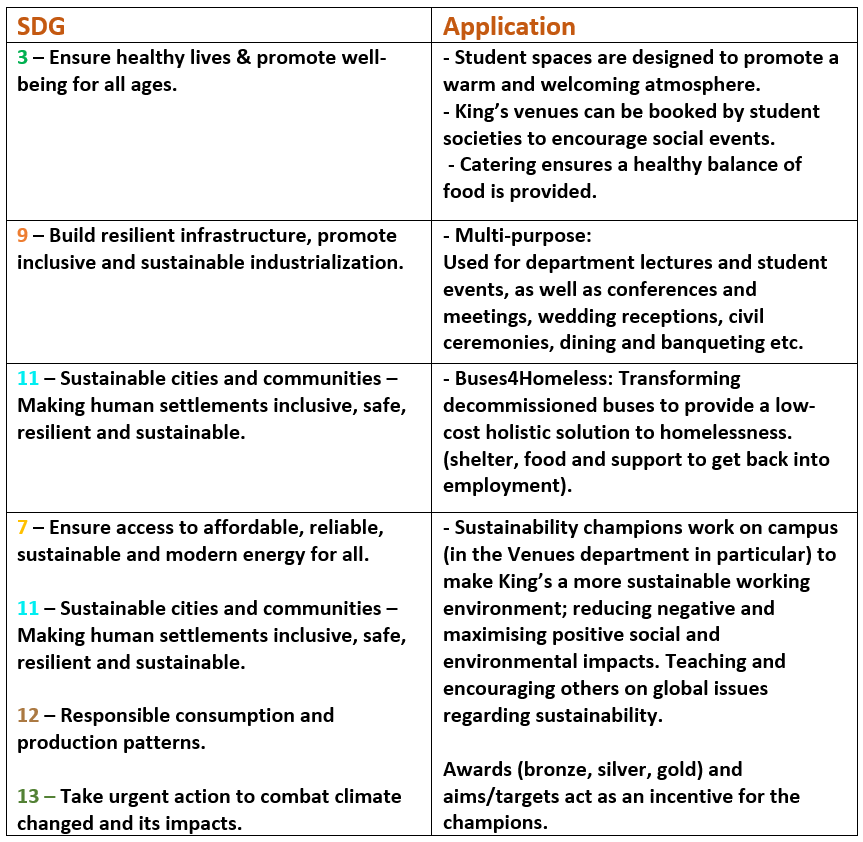
This guest blog comes fifth in a series of blogs on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) courtesy of Onna Malou van den Broek, second year doctorate student at King’s in the European & International Studies Department. Onna’s doctorate project titled: ‘The Political Payoff of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): CSR as a Determinant for Lobbying Success’, which looks at the relationship between corporate sustainability and lobbying, holding a special focus on the SDGs.
Can you still recall the ‘beast from the east’? Last year, London was ravaged by snowstorms and temperatures dropping far below zero. Thames Water was unprepared which resulted in burst water pipes in the South West. My apartment was cut off from water for almost a week. This week I realized how dependent we are off water. I couldn’t shower, do the dishes, cook, clean, drink tap water or go to the toilets anymore. Globally, water scarcity is an enormous issue. This month I will zoom in on SDG 6: clean water and sanitation.
SDG 6: Access to clean water and sanitation
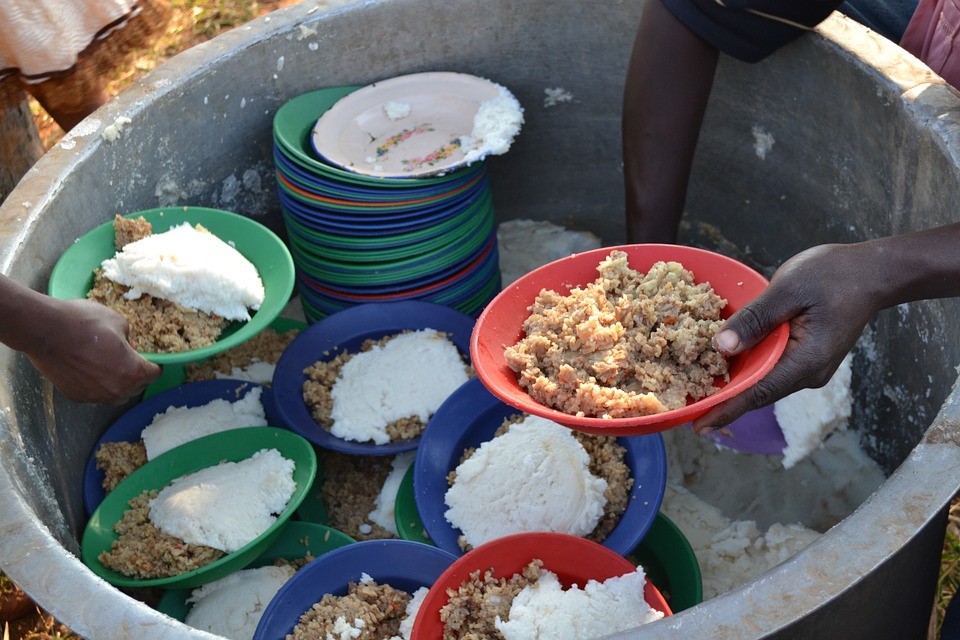
Clean drinking water and adequate sanitation are essential to survive and live a dignified life. In 2010 the UN, therefore, decided to include water as a human right (1). Clean water is not guaranteed: 2.4 billion people don’t have access to sanitation and 1.8 billion people use polluted water. Water scarcity affects over 40 per cent of the global population. Due to climate change and population growth, this number is expected to rise even further (2). Inadequate water facilitates have big health consequences. They lead to poor hygiene, which causes various diseases. Every day, 800 children still die from diseases caused by poor sanitation. This is unnecessary.
The targets: Access, quality and efficiency.
The targets focus on the necessity of clean water in our everyday lives and the treatment of global water resources (3). Foremost, there needs to be universal access to safe, equitable and affordable drinking water and sanitation. This includes ending open defecation in order to avoid breed places for bacteria, which disproportionally affects the health of women and girls. Furthermore, water quality must be improved by reducing (chemical) pollution and safely reusing wastewater. All sectors need to increase water-usage efficiency and states need to implement integrated water resources management and protect water-related ecosystems, such as wetlands, rivers, and lakes. This can only be achieved through international cooperation and strengthening the participation of local communities.
UN water study: Find solutions within nature.
In 2018 the UN released a study on Nature-Based Solutions (NBS), which refers to finding solution to water scarcity that are inspired and supported by nature. As such, they aim to exploit opportunities that harness natural processes (green infrastructures) which regulate various elements of the water cycle. An example of an NBS that helps manage water availability is the creation of urban wetlands in order to reintroduce used water into the ecosystem. Another example is the creation of underground water reservoirs that can be used during droughts (4). Despite their enormous potential, NBS unfortunately only encompass one per cent of the total investments in water management.
Measuring water pollution on your smartphone.
Through the European partnership ‘MONOCLE’ researchers strive to use earth observation and data to monitor water quality (5). Participants are currently developing low-cost optical sensors, methods and technologies to support water quality monitoring by regional and national agencies. In addition, they explore the role that local volunteers can play in collecting environmental data. The idea is that by tapping into people’s own devices, citizens can provide much needed data. One project, which is led by my former university in Leiden, is ‘iSpex’. Through a mass producible add-on for smartphones with a corresponding app, volunteers will hopefully be able to monitor air and water quality properties in the future.
SDGs: Water, poverty and woodlands.
The SDGs are highly interconnected and can’t be seen separately. Water is essential for achieving any other SDG. As such, clean water is a requisite for health, gender equality, food production, energy supply, economic growth, biodiversity and tackling climate change. Water shortage and poor hygiene disproportionally affects vulnerable societies. Regions that battle with poverty, such as Sub-Saharan Africa, are characterised by long periods of drought (6). This directly impacts the quality of their land: water shortage and pollution destroy ecosystems. As a result, regions end up in a vicious circle: a. poor countries are often dependent on agricultural, b. land degradation destroys fertile soil making land unusable for agricultural, c. this process is accelerated by water shortages.
Reduce your water consumption!
Every day, we consume huge amounts of water, both directly and indirectly. On average, one person uses 121 litres of water per day: 6 litres per toilet visit and 10 litres per minute spent under the shower. In addition, the production of our food and products requires larges amount of water: 2,400 litres of water are needed to produce one hamburger and 11,000 litres to produce a pair of jeans. You can contribute to achieving SDG 6 by:
- Changing your behaviour regarding water consumption. For example, close the tap while brushing your teeth; use a bowl when doing the dishes; flush the toilet only once; and spend a minute less under the shower.
- Investing in innovative products that use less water. For example, there is a shower head that can save up to 2 litres of water per minute!
- Being conscious about water requirements for food and other products. For example, try to eat an extra night of vegan or vegetarian food, or buy a pair of jeans that will last more than one month.
- Inform yourself! Knowledge is power, so make sure you know your facts. You can, for example, follow a course at Coursera on Water Resources Management and Policy from the University of Geneva or on Water Supply and Sanitation Policy in Developing Countries by the University of Manchester.
Resources
(1) Access to water as a human right: www.un.org/waterforlifedecade/human_right_to_water.shtml
(2) For more information, read the ‘why it matters’ spreadsheets: www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/6_Why- it-Matters_Sanitation_2p.pdf
(3) For an overview of all the targets: sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdg6
(4) The UN NBS rapport: unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0026/002614/261424e.pdf
(5) Read more about Monocle: monocle-h2020.eu/Citizen_science
(6) A map with global water shortages: www.wri.org/our-work/project/aqueduct/maps-data