Each year, we hold Sustainability Week to raise awareness and educate King’s staff and students about sustainability at King’s. Sustainability Week revolves around ‘#MakeADifference’. The Sustainability Team, alongside student societies and staff Sustainability Champions, put on events with the aim to educate on various areas of sustainability (social, environmental and economic), give back to society and most of all – have fun!
Here is a summary of the week…
Sustainability Pop up: This Sustainability Week we hosted an interactive stall across King’s campuses. We played lots of sustainability related games –
we quizzed you on how many of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SGDs you could remember and played the washing line game, where staff & students got the chance to win a Keep Cup and a free tea/coffee if they correctly guessed how long it took seven everyday items to degrade (from tea bags, to tin cans (hint: they rust!) to plastic bags). It was great to talk with staff & students about what interests you most within sustainability and we got the chance to update staff & students on some of the sustainability projects happening at King’s – for example, the Don’t Be Trashy project and behaviour change techniques aimed to reduce waste and increase recycling rates in King’s halls of residences.

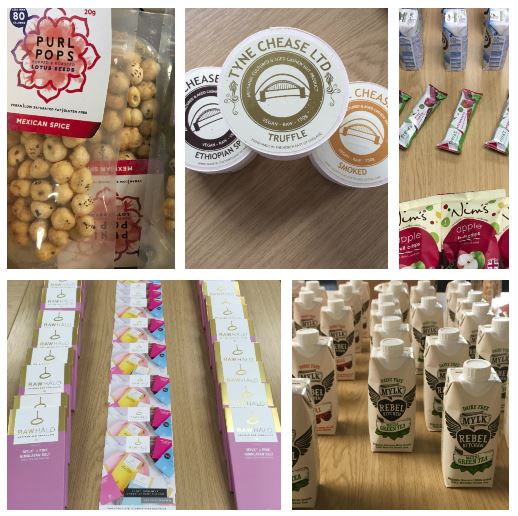
King’s VegFest: Studies show that a veganism can reduce the environmental impact that your diet has, and reducing the amount of meat and dairy we consume can positively affect climate change. We hosted this event in collaboration with the King’s Vegetarian and Vegan society. There were lots of free samples from vegan producers, including vegan cheese (thank you Tyne Chease), chocolate (thanks to Raw Halo) snacks (thank you to Purl Pops, Nim’s Fruit Crisps and Freya’s Fruit Bars), Dairy Alternatives (thank you KoKo, Rebel Mylk and to a King’s Alumni own brand: Edenera!). Students and staff also brought delicious dishes for everyone to try, we discussed the environmental impact of the food we eat and general sustainability passions!

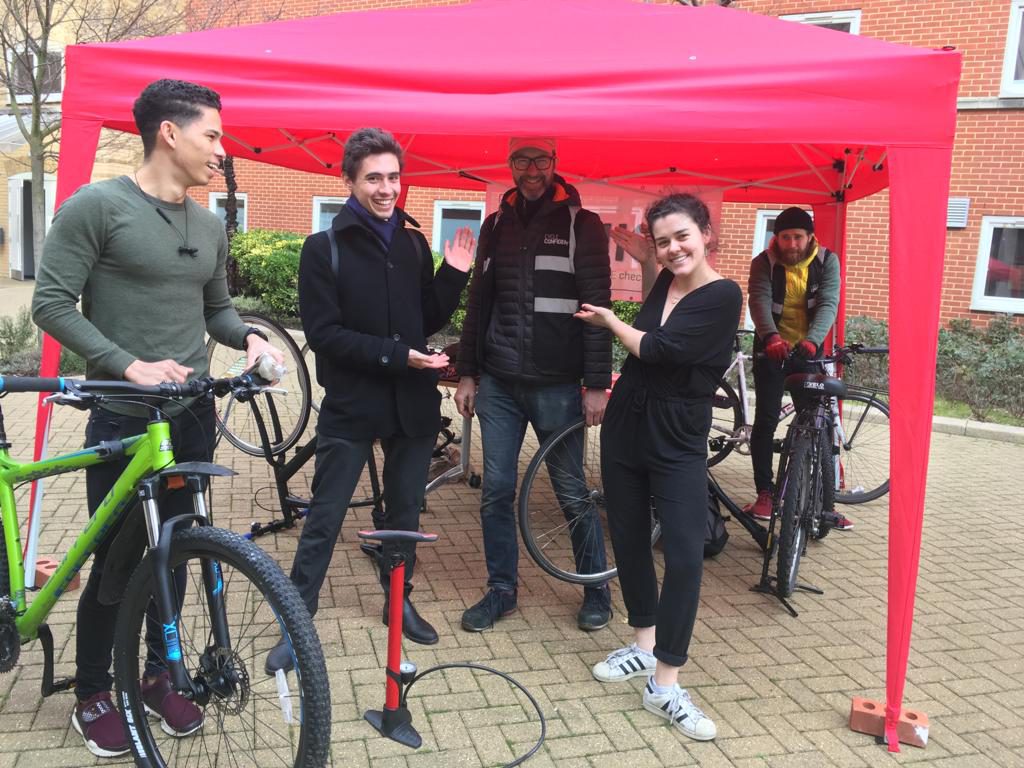
Dr Bike: Cycling is not only an environmentally sustainable form of transportation, but one that is socially sustainable due to the value exercise has on physical health and overall well-being.
We want to encourage cycling in London and help make it as easy as possible for our staff and students. Therefore, we held four Dr Bike sessions across the King’s campuses. These Dr Bike sessions provided free bike checks to students and staff. Mechanics led the session and checked brakes, gears and chains, changed bike pads and gave advice and accurate quotes for whatever they couldn’t fix. There are many Dr Bike sessions happening across London every day, organised through Cycle Confident. To keep up to date with the latest session near you, follow Cycle Confident updates here.

Film Screening: A Northern Soul: Sustainability often gets bundled into being thought of as purely environmental, with the social and economic sides to it often neglected. This year, for our final event of the week, we chose a film which demonstrated the importance of these two, often forgotten, pillars of sustainability. A Northern Soul is a documentary set in Hull, which follows one man, Steve, a warehouse worker on his journey through Hull in 2017 during its crowing year as the ‘UK City of Culture‘. We see Steve chase his passion of bringing hip-hop to disadvantaged kids across the city, through his Beats Bus. The film raises uncomfortable truths about inequality in the UK, but does so while demonstrating the strength and charm of Hull’s residents in the face of this inequality. The film is available on BFI player.

GoodGym Run: King’s GoodGym is a community of runners that combines getting fit with doing good. For this session the runners went to Euston Food Bank. GoodGym volunteers helped to sort out the dry donations of cereal, biscuits and chocolate into sell by date to help ensure no food loss and effective allocation of items according to date. King’s GoodGym is a great way to get fit and to help the local community. To read more on GoodGym click here.

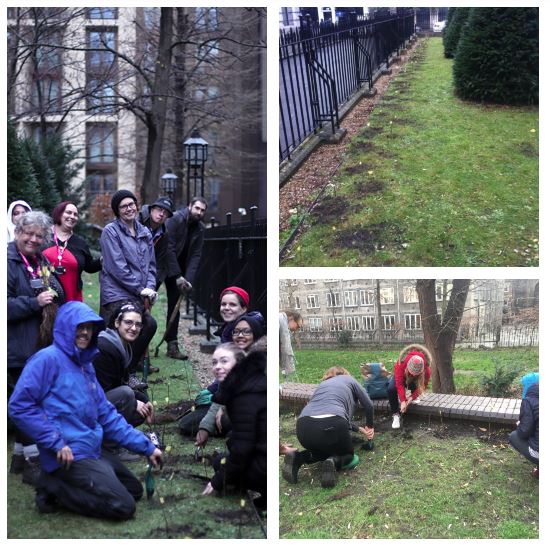
Gardening at the Maughan: The Library Services Sustainability Champions ran the gardening session at the Maughan to help nurture the 200+ trees which were planted in the garden at the start of December 2018, as part of National Tree Week and broader City of London Environment and Clean Air Strategies . Sustainability Week volunteers watered all the trees and
re-taped them to ensure their visibility, helped to replant some of the crab apple trees and gave the garden a quick litter pick – all in all, the garden got a good bit of T(ree)LC.

Ethical Beauty Talk: Stephanie Green from the Modern Language Centre spoke about how sustainable shea butter can empower women. Speaking from her experience living and working in Ghana she told the story behind the TAMA brand, made from natural shea butter. Lots of the beautiful vegan friendly soaps, creams and lotions were also available for sale at the session!

Zero- Waste Beauty Workshop: 8 million tonnes of plastic end up in the ocean every year. The UN has stated that our use of plastic is creating a ‘planetary crisis’, and by 2050, the oceans will carry more plastic than fish. Read more here.
During the week, we held two zero-waste workshop sessions, co-hosted with the King’s Beauty Society. In these sessions, students learnt more about the global plastic-problem and the individual steps we all can do to make zero-waste living that little bit more achievable. Students got to make their own zero-waste coffee body scrub (using King’s Food own used coffee grounds – which would have otherwise gone to Anaerobic Digestion), lemon lip scrub and peppermint toothpaste!
Due to the demand, The Sustainability Team plan to host more events like this throughout the year. In the meantime, a post with the zero-waste beauty recipes will follow on the blog soon.

Top right: Essential oils used for the toothpaste and lip scrub
Bottom Left: Breakdown composition of the coffee body scrub (1/2 coffee, 1/4 sugar, 1/4 coconut oil)
Bottom Right: President of KCL Beauty Soc
Thank you to everyone who helped organise and took part in Sustainability Week 2019! We love meeting you all and hearing your feedback, ideas and passions. You showed King’s really can #MakeADifference!