This guest blog comes fifth in a series of blogs on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) courtesy of Onna Malou van den Broek, second year doctorate student at King’s in the European & International Studies Department. Onna’s doctorate project titled: ‘The Political Payoff of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): CSR as a Determinant for Lobbying Success’, which looks at the relationship between corporate sustainability and lobbying, holding a special focus on the SDGs.
Mornings are not my finest hours. With the winter around the corner, I put the heather up and turned on the light to watch the news on my laptop. I quickly boil an egg, toast some bread and jump into the bus to King’s College. Energy is for most of us (including me) a given, but while we are polluting the planet by burning fossil fuels many people are still energy deprived.
SDG 7: Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy
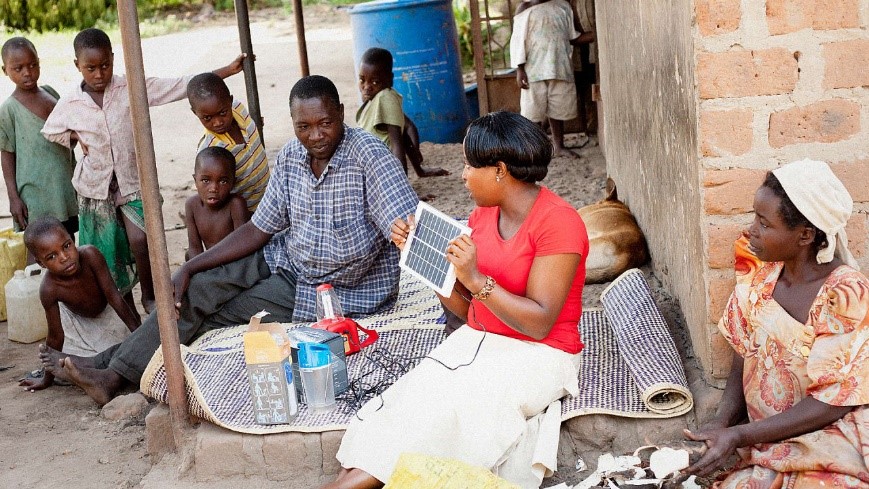
Energy poverty constraints everyday live and limits human and economic development [1]. Worldwide, around 840 million people do not have access to a reliable electricity source. Moreover, 3 billion people do not have access to clean cooking fuels causing indoor pollution endangering health. Energy also supports the working of practically every economic sector: from businesses, medicine and education to agriculture, infrastructure, communications and high technology. At the same time, many economies are dependent upon fossil fuels, that is coal, oil and gas. These fossil fuels produce large amounts of greenhouse gases which is a main contributor to our current climate crisis.
The Targets: Global access to CLEAN energy
Energy is both a social and an environmental problem [2]. This reflected in the underlying tensions of the targets: we want people to have universal access to affordable and reliable energy services, however, the energy sources need to increasingly be renewable and used efficiently. Whereas advanced economies need to adapt their current supply systems, developing economies are hoping to leapfrog directly into clean energy systems. Governments, therefore, need to invest and share clean energy technologies as well as expand clean energy infrastructures.
What is renewable energy and why is it important?
The word ‘renewable’ underlines the access problem we face; at some point in the near future we will run out of fossil fuels and therefore we need to find energy sources that can be constantly replenished [3]. However, there is also an environmental component as fossil fuels are the number one cause of global warming (SDG 13). Renewables can meet our energy needs without harming the earth because they release very few chemicals, like carbon dioxide. New technologies are able convert renewable resources, such as the movement of the wind and water, the heat and light of the sun, the carbohydrates in plants, and the warmth in the Earth, into electricity. The good news is that renewable energy consumption has increased from 16.6 per cent in 2010 to 17.5 per cent in 2016. However, if we want to achieve the climate goals, this change needs to be rapidly accelerated.
The Boy who Harnessed the Wind
The Netflix movie ‘The Boy Who Harnessed the Wind’ beautifully brings the energy problems to life. It tells the story of a 13-year-old boy who is thrown out of the school when his family is unable to pay his fees. With help from his former teacher, he gets access to the school’s library where he learns about electrical engineering and energy production. Seeking to save his village from the drought and famine, William plans to build a windmill to power an electric water pump to sow crops (SDG 6). Through Williams experience, we see the importance of light for studying, the effects of global warming and the necessity of horsepower to survive draughts [4].
Solar Sisters: Women’s Entrepreneurship for Sustainable Energy
Energy poverty and climate change is disproportionally shouldered by women (SDG 5). They are often responsible for collecting fuels and suffer the health consequences of unclean cooking fuels. Solar Sister [5] invest in women’s enterprises in off-grid communities to deliver clean energy. They provide finance, training, technology and services that enable women to build sustainable businesses. This way, they create a ripple effect impacting not only local women but also their families, and the customers and communities who switch to using clean energy. They kickstarted 4.000 clean energy entrepreneurs and impacted 1,5 million people across Africa.
The Goals are there for You!
Living and studying in the UK, your biggest impact is most likely on clean energy production and consumption. As such, you can take a critical look at you:
- Energy supplier – Who supplies your energy? What is their energy mix? Can you change to more clean energy providers? Good examples of green UK energy providers are: Ecotricity, Bulb, Ebico and The Utility Warehouse.
- Energy consumption – There are many small steps to take in your day-to-day live, for example turn off your laptop; unplug electronical devices that you are not using; don’t leave chargers plugged; or change your bulbs to LED lights.
- Investments – Many students forget that their savings are invested in energy production. Does your bank still invest in fossil fuels, or do they encourage clean energy? Alternatively look in what your university or parents are investing. Did you know that KCL is committed to divest from all fossil fuels by the end of 2022 after students’ hunger strikes?
[1] A facts sheet on why this goal is so important can be found here: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Goal-7.pdf
[2] You can read more on the targets and how we are currently doing here: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdg7
[3] Learn more about renewables and fossil fuels and their impacts here: https://www.ucsusa.org/energy
[4] You can watch the movie on Netflix, but here is a small trailer to convince you: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=izCc4duhnxA
[5] Learn more about the great work Solar Sisters are doing: https://solarsister.org/about-us/