Author: Alexandra Hepple (Page 2 of 7)
To the new students joining King’s this September, welcome! We hope you’ll really enjoy your time at King’s, there is some much going on and there is truly something for everyone.
If you’re as passionate about sustainability as we are, here is a round up of a few things Sustainability at King’s has achieved so far – or plans to achieve (which you can be part of and support on too!):
- King’s has a target to reduce it’s carbon by 43% by 2020 (from it’s 2005/06 baseline).
- King’s has a net-zero carbon target set for 2025.
- As of August 2020, a King’s Climate Action Network (CAN) has been established so students and staff can actively shape how King’s will achieve it’s net-zero carbon target by 2025. Form to join the network here.
- Since 2017, King’s electricity has come from 100% certified renewable sources (wind power!).
- The Sustainability Champions programme aims to influence behaviour change and empower our King’s students and staff to make the sustainable changes on the ground in their areas (whether that is an office, a classroom, research or teaching lab or a halls of residence). We started the programme in 2014 – starting with 17 champions, there are now 532 students and staff taking part.
- You can apply to be a Sustainability Champion Assistant (role will be advertised on KCLSU volunteer platform – end of October/early November) – to help a staff champions team embed sustainability in their area and create projects you want to see introduced!
- King’s has increased it’s recycling rate from 37% to 69% in 2020 (pre-COVID lockdown).
- King’s Sustainability has now produced 3 Sustainability Reports – see them here for a more detailed look at how far we’ve come – but also where we still need to get to!
- Sustainable Food is important to King’s – it has now achieved it’s second ‘Michelin star of sustainability’ – given by the Sustainable Restaurant Association.
- As part of the King’s Sustainable Food journey, you can attend the quarterly Sustainable Food and Fairtrade Steering Group meetings – to hear about what is going on in the world of sustainable food at King’s and suggest any ideas or projects you want to start.
- Worked with King’s College Student Union (KCLSU) to establish a Sustainability team in the Union Development Committee – a group of 9 students, democratically elected each academmic year to improve the sustainability of the SU.
- Created a Biodiversity Action Plan for all four campuses and sports grounds.
- Sustainable communications – since Sept’ 2018, we have had 31 guest blogs written and published King’s students and staff on the Sustainability blog.
Finally, make sure to get in touch with us at sustainability@kcl.ac.uk if you have any questions/ideas – and make sure to subscribe to the Sustainability Newsletter to keep updated on events, volunteering opportunities and more!
This guest blog comes from Sarah Gold, MSc student, studying Sustainable Cities.
Why environmentalism needs to be intersectional
On 28th May, three days after the murder of George Floyd, climate activist Leah Thomas shared a post on Instagram which quickly went viral, popularising the term ‘intersectional environmentalism’, a type of environmentalism which takes into account the ways in which social and environmental justice overlap. In this blog, I explain why an inclusive, anti-racist approach is vital to the environmental and climate justice movement and where we can all learn more.
What is intersectional environmentalism?
‘Intersectionality’ was coined in 1989 by Kimberlé Crenshaw, an American lawyer, civil rights advocate and leading scholar of critical race theory. The term describes how multiple forms of injustice, such as racism, sexism, ableism and countless others, overlap or ‘intersect’ with each other. These inextricably linked systems of oppression present in our society mean that some individuals will simultaneously face several sources of discrimination.
For instance, as a woman I will inevitably confront sexism throughout my lifetime, however due to my white and other privileges, there are many other forms of oppression that I do not have to face on a daily basis.
Intersectional environmentalism, then, is the concept that environmental issues do not exist in a vacuum, but cross paths with other forms of injustice. According to Leah Thomas, it is defined as “an inclusive version of environmentalism that advocates for both the protection of people and the planet. It identifies the ways in which injustices happening to marginalised communities and the earth are interconnected. It brings injustices done to the most vulnerable communities, and to the earth, to the forefront and does not minimise or silence social inequality. Intersectional environmentalism advocates for justice for people + planet”.
Intersectionality is a powerful tool to connect environmental activists with other social movements such as feminism, Black Lives Matter (BLM) and LGBTQ+. Working together helps to amplify each movement’s voice and create meaningful long-lasting change.
Why is intersectional environmentalism important?
In the past, environmentalism has typically been associated with and dominated by white, middle-class males. At best, this means mainstream environmental movements and NGOs have too often shied away from acknowledging the racial dimension of issues such as air and water pollution; at worst, this can mutate into ‘ecofascism’, a disturbing white supremacist ideology that considers racial purity to be the solution to environmental problems.
The danger of ecofascism was clearly demonstrated in 2019 when two of its adherents committed public shootings in El Paso, Texas and Christchurch, New Zealand. Opening up the environmental movement to all races and minorities and educating ourselves on racism are necessary steps to address this problematic past and present, and the privilege associated with participating in environmental struggles.
Whilst white people are more likely to be able to afford a ‘sustainable lifestyle’, minorities are more likely to be on the frontline of the worst environmental problems. The environmental justice movement that emerged in the late 1970s in the USA first drew attention to the disproportionate environmental burdens borne by economically disadvantaged and minority communities.
In 1976, the ‘Love Canal’ case gained international media coverage for having caused significant detrimental health effects in residents of a working-class area in Niagara Falls, New York that had been built on top of a toxic landfill site. This was the first well-documented example amongst many of the increased exposure to polluted and noxious environments experienced by minorities.
A study in 2016 showed that London’s black, African and Caribbean communities are disproportionately exposed to air pollution, and are more likely than white people to breathe in illegal levels of nitrogen dioxide, a harmful pollutant responsible for increased rates of respiratory problems, particularly asthma in children.
Climate change is no exception to this trend. The climate crisis will – and already is – increasing both global and local inequality. The effects of climate change will hit hardest those least responsible for global warming in the Global South. Australia being the only exception, countries with lower GDPs will warm the most. The effects will be also felt disproportionately by marginalised communities in the Western world.
Non-white people are currently experiencing the worst environmental problems in our world. In the U.S., Black and brown communities are more likely to live near toxic waste sites, live in communities with fewer environmental amenities, be harmed by climate change, inhale fine particulate matter and more. Globally, indigenous people and people living in island nations and Central Africa are facing the brunt of climate change and waste dumping. Likely due to this first-hand experience, a recent study found that Black and Latinx people are much more concerned about climate change than white people. Witnessing the toll of environmental issues can help environmentalists more fully understand the problems we’re facing and share in these communities’ concerns. And amplifying stories from these minority communities can hopefully convince policymakers that these environmental issues are real and deserving of immediate attention.
The book ‘Why Women Will Save the Planet’ highlights how women are likely to be most adversely affected by climate change too, particularly in poor and marginalised communities in developing countries, since they often depend on climate-sensitive livelihoods such as agriculture, securing water, food and fuel, and are often the last to evacuate their homes when natural disasters strike, leading to higher mortality rates.
Although these are just a handful of examples of the manifold ways in which minorities are more likely to suffer the consequences of environmental crises, it illustrates the importance of adopting an intersectional approach – it is impossible to extricate them from socioeconomic issues. It is worth reminding ourselves that sustainable development, the holy grail of many environmentalists and human geographers, is based not just on environmental, but economic and social sustainability too.
Where can I learn more about intersectional environmentalism?
As a white environmentalist, it is more important than ever to ‘do the work’ and hold myself accountable! Here are some incredible intersectional and anti-racism environmentalists that have inspired and educated me so far.
- Leah Thomas, @greengirlleah, shares informative content on climate justice and intersectional environmentalism, the term she popularised online.
- Check out the Intersectional Environmentalist platform which Leah co-founded. It’s a website full of information on how to dismantle systems of oppression in the environmental movement, with resources aimed at a growing number of communities (at the moment it includes Black, Latinx, U.S. Indigenous, LGBTQ2S+, South Asian and allies).
- Pattie Gonia, @pattiegonia, who describes himself as an “intersectional environmentalist, ally-in-progress and fetus drag queen” is also one of the co-founders of the Intersectional Environmentalist platform and has some great content on allyship.
- Mikaela Loach aka @mikaelaloach uses her voice on Instagram to talk about inclusivity in sustainability as well as anti-racism, anti-ecofascism and feminism. She is also co-host of the brilliant @theyikespodcast which I highly recommend! Their episodes have covered topics including the links between coronavirus and ecofascism, fast fashion, BLM, and going beyond white environmentalism.
- You can also find Marie Beecham at @wastefreemarie for actionable tips for zero-waste living and information on climate and racial justice.
- Who doesn’t love a good TED talk? Check out Kimberlé Crenshaw’s TED talk on intersectionality, for a great 20 minute introduction to the concept. And if you’ve got just 7 minutes to spare, watch 17-year old youth striker Isra Hirsi’s TED talk on being the ‘Angry Black Girl’ in the climate justice space.
Please feel to add to this list, share with others and start conversations with your friends and families!
Each year, we hold Sustainability Week to raise awareness and educate King’s staff and students about sustainability at King’s. Sustainability Week revolves around how to ‘#MakeADifference’. The Sustainability Team, alongside students, student societies, staff Sustainability Champions and charities, put on events with the aim to educate and inspire around various topics relating to sustainability (whether that be social, environmental or economic), give back to society and most of all – have fun!
We had a total of 522 people come to take part in the events throughout the week.
Here is a summary of some of the events we had throughout the week…
GEOGFEST
GeogFest’ was a charity event for King’s staff and students, organised by GeogSoc and the Geography Sustainability Champions to raise money for the International Tree Foundation.
The even t took place in the KCLSU bar The Vault on Friday 7th February as an early kick of to Sustainability Week.
t took place in the KCLSU bar The Vault on Friday 7th February as an early kick of to Sustainability Week.
There was entertainment from the Worn out Shoes ceilidh band formed by academics from across the Geography department, PhD candidate George Warren and a dance materclass by UG student Pia Fletcher.
There was a live count of the money raised through the night, in total the Geography department raised £243.38 for the ITF, which will be used to help offset the flights from second year Portugal and Morocco fieldwork trips.
DIY lip balm & craft your own zero-waste products
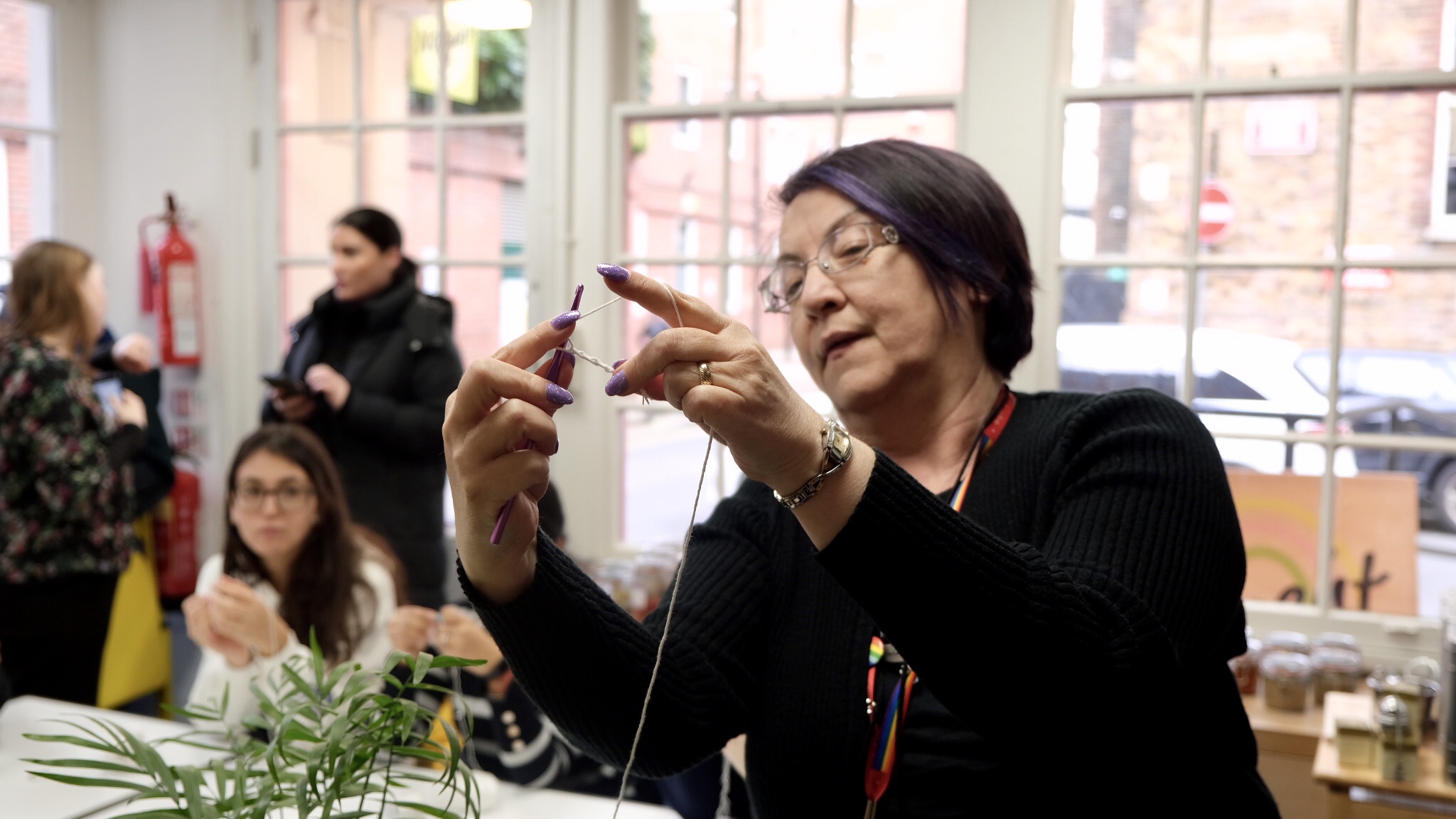
Gathered in the KCLSU zero-waste store, Nought, 24 students got together to learn how to make their own zero-waste lip balms (recipe here – made without the honey) and how to crochet their own face scrubbie, instructed by King’s Energy Manager and star crafter, Julie Allen.
During sustainability week, Nought held a competition to win a zero-waste hamper for all those who spent over £10 – so this event was also a chance for the students to stock up on their essentials to be in with a chance to win!
A Green Threaded Corridor
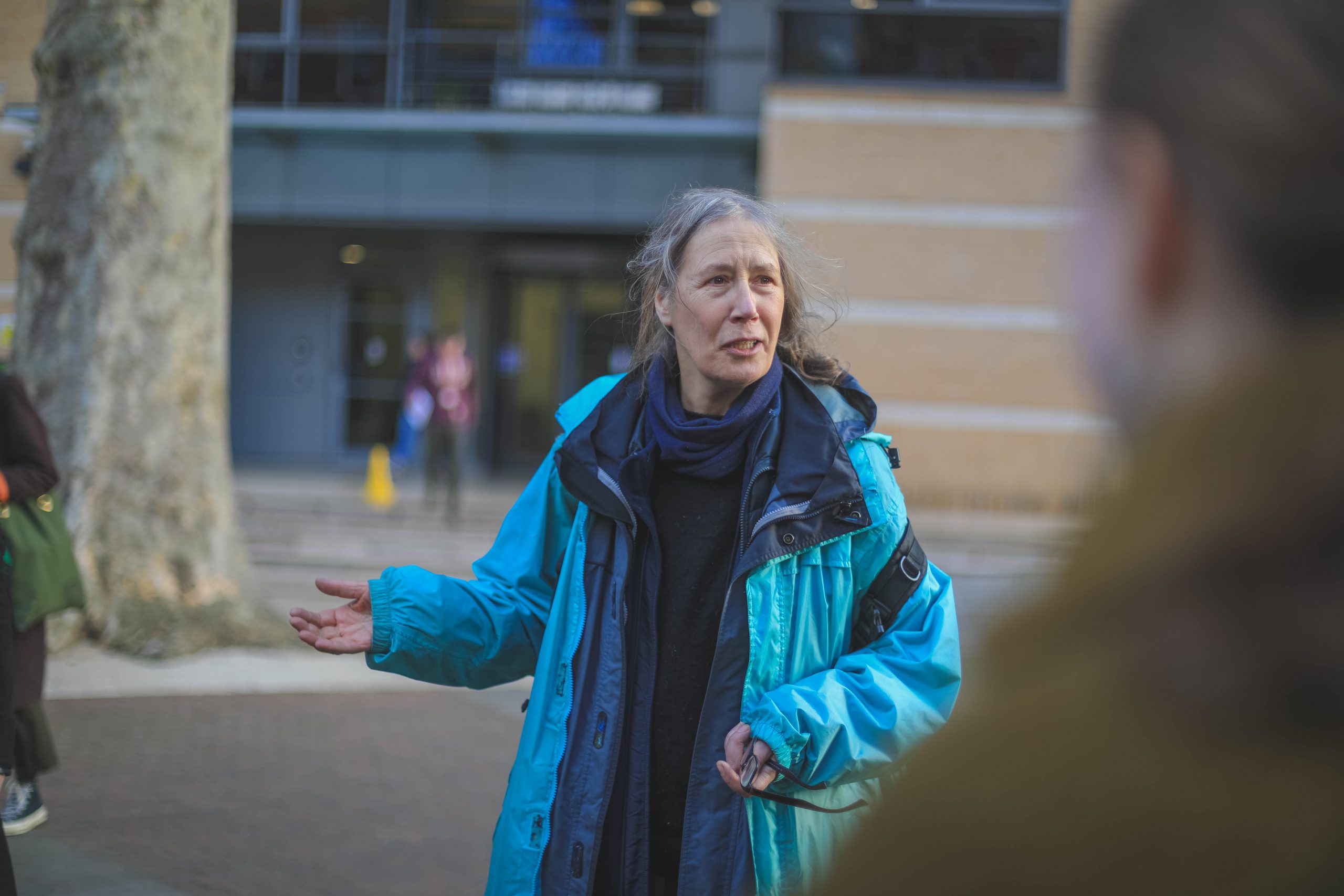
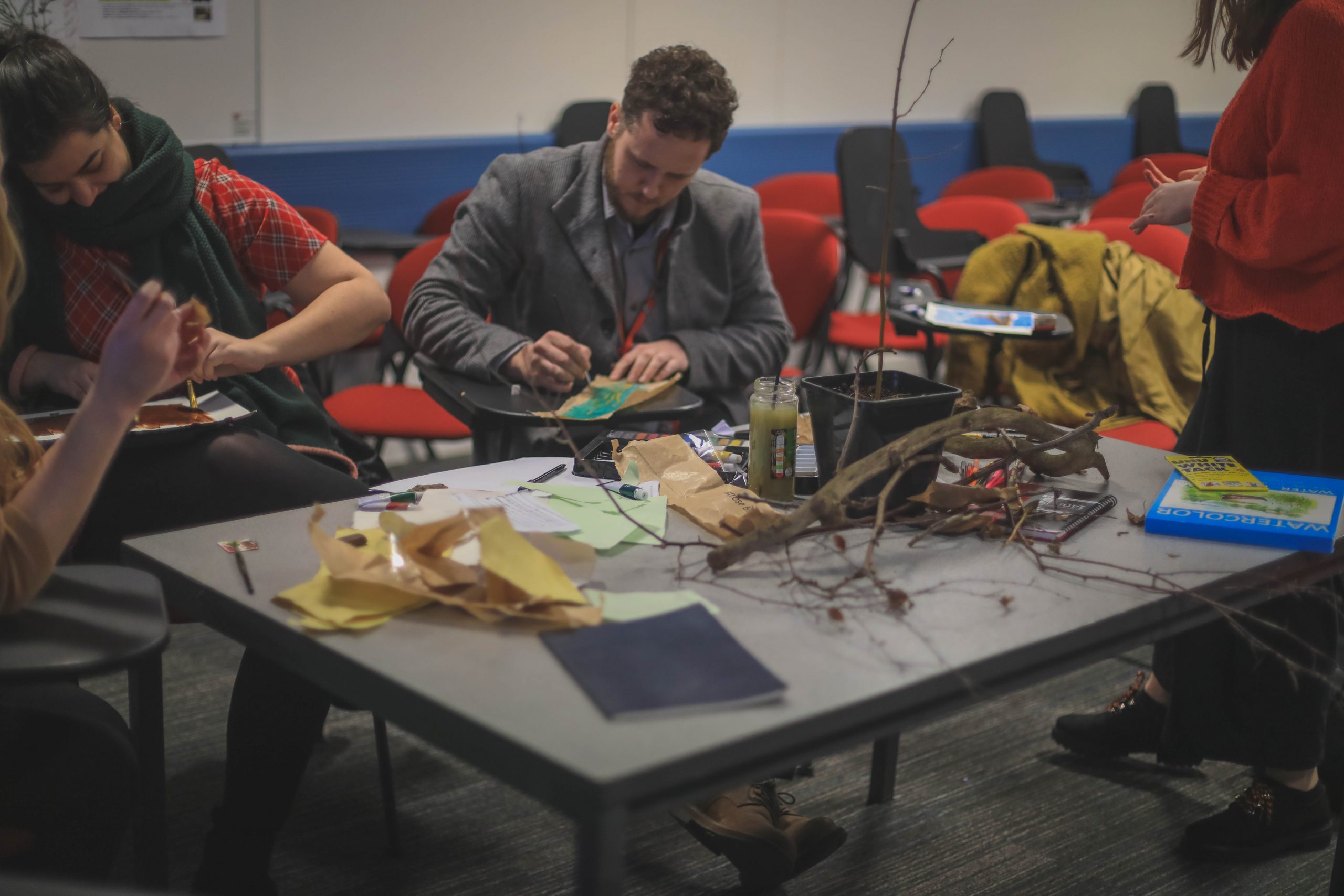
Artist and Goldsmiths University student, Margaret Jennings came to Kings to deliver ‘A Green Threaded Corridor: Tree Art Workshop’. The workshop started with a conversation about our natural environment in the middle of Guy’s campus memorial garden and an insight into Margaret’s background and artwork. This was followed by a silent walk around the gardens, taking notice of the trees and life which surrounds them.
Natural materials from the gardens were gathered and used in the art section of the workshop. The art was inspired by our individual tree stories (e.g. a cherry tree in a grandfathers garden or the grief you feel when a tree is cut down) – the art could be painting, drawing, poems. These were passed around and altered by others – as a comment to nature and its ever evolving state.
The art and poems created in the workshop will form the body of Margaret’s research at Goldsmiths university – alongside other university and community group tree stories.
The event ended with planting a Birch sapling on Guys Campus gifted by Goldsmiths University. This will form part of a tree corridor, as King’s will be mirroring this by gifting an Alder tree to Goldsmiths University.
King’s Think Tank: Post-Environmental Regulations Debate
See the blog post below, for an event summary from the Director and Researcher of the King’s Think Tank Energy and Environment policy centre.
Vegan Sushi Class
King’s Vegetarian and Vegan society ran a vegan sushi class at Great Dover Street Apartments (GDSA) café. Over 30 students came to learn how to make their vegan sushi from scratch – how to cook the perfect sushi rice, prepare the vegetables, tofu or tempeh and do the perfect sushi roll.
Circular Economy Workshop with the Ellen MacArthur Foundation
 On the final day in Sustainability Week, the Ellen MacArthur Foundation came to deliver a workshop on circular economy.
On the final day in Sustainability Week, the Ellen MacArthur Foundation came to deliver a workshop on circular economy.
They gave attendees an overview of what the circular economy is, and what businesses and services using circular economy principles may look like. As it was Valentine’s Day, they tasked students with coming up with circular economy alternatives to common Valentine’s presents, including re-used cards and potted flowers.
Each year in March, students, staff and alumni take part in a range of volunteering activities across the world as part of King’s Global Day of Service.
This year, King’s Global Day of Service is on Wednesday 25th March (to celebrate the day King’s was founded) but any volunteering activities that take place throughout March can contribute to GDoS volunteering hours.
King’s is the first university in the UK to run Service events at this scale and the King’s GDoS activities represent our commitment to serving local, national and international communities.
The 2019 GDoS involved 190 volunteers in nine Service events in London and fifteen international events, across five continents. In total, 635 Service hours were completed, with an estimated economic impact of £5,000.
Find out more about what you can get involved in at King’s and across London this 2020 GDoS, here.
This guest blog comes from Mathilde Funck Brentano and Irina Tabacaru who are the Director and Researcher at the King’s Think Tank Energy and Environment policy centre.
On Tuesday 11 February, the Energy and Environment Policy Centre hosted an exclusive panel event as part of King’s College London’s Sustainability Week. We welcomed Scott Ainslie (Former Green Party Member of the European Parliament), Adam Bartha (Director of EPICENTRE), and Professor Robert Lee (Director of the Centre for Legal Education and Research at the University of Birmingham) to discuss the future of environmental policies in the United Kingdom in the post-Brexit era. The three speakers answered multiple questions, notably on the strengths and weaknesses of the European Union’s environmental law, as well as more specific topics such as air pollution and energy policies. The speakers clearly expressed their perspectives and gave the audience a fascinating insight into the post-Brexit debate on environmental regulations.
The Energy & Environment policy centre began the event with an audience-directed poll, featuring the question: ‘Do you think the UK should move forward with stricter environmental regulation after Brexit?’. After some time to reflect, the majority responded in favour of stricter regulation.
Following the survey, the panel began by discussing whether the UK should uphold European environmental standards after Brexit. While the speakers displayed little confidence in the ability of the current UK government to expand environmental regulations, all three argued in favour of furthering the existing policies. Drawing from his experience as a specialist advisor in the drafting of environmental legislation in Northern Ireland and Wales, Professor Lee highlighted the importance of compromise in reaching higher-level objectives in environmental regulations. In order to enable effective policies to be successful, the accessibility of environmental regulations ought to be improved. The discussion also mentioned the importance of changes in consumption habits to match governmental policies. Mr. Bartha expressed optimism regarding the United Kingdom’s prospects after Brexit. As he noted, one of the European Union’s main weaknesses is its bureaucratic aspect, and the fact that European policies are not implemented by all member states evenly. For example, member states in Eastern Europe respond differently to environmental policies than those in Northern or Western Europe. The United Kingdom now has the possibility to expand sustainability-related regulations more freely across its territory, and avoid the European Union’s precautionary principles in the drafting of legislation, as well as the excessive allowances of the Emissions Trading System (ETS). Conversely, Mr Ainslie underlined the apparent lack of ambition demonstrated by the British government in regard to green policies, particularly when compared to European targets. The speakers also discussed the necessity of a kerosene tax, given the considerable amount of carbon dioxide emissions generated by air transport.

The discussion continued around the themes of Energy and Air Pollution. There was considerable disagreement between the speakers regarding the use and safety of shale gas as a potential alternative energy resource for the UK. The speakers’ views also diverged on the possibility of the UK reaching one hundred percent renewable energy use in the near future. Professor Lee also mentioned the importance of the UK finding its position concerning access to EU energy and, more importantly, pan-EU energy sources.
Our speakers expect that air quality standards will be upheld in the United Kingdom, despite its departure from the European Union. The British government has been tried several times by the European Court of Justice for failing to respect air quality standards. There is considerable public awareness on the topic, with approximately 28,000 to 36,000 pollution-related deaths in the UK every year. The necessity of tight cooperation between Westminster and local governmental bodies was put forth, as well as the urgent need for further enforcement.
Following the panelists’ discussion, the floor was opened to questions. The audience was extremely engaged in the discussion and interacted with the three panelists, raising a variety of issues, including the possibility of an EU-level meat tax. A captivating debate occurred regarding the theme of individual responsibility for climate change, as opposed to corporate and governmental responsibility. The high costs of sustainable and organic products, which represent a true burden for the average consumer, were extensively considered. The topic of waste management was also raised, following China’s decision to close its borders to foreign waste. Our panelists disagreed regarding the existence of the concept of ‘cyclical economy’, especially with reference to vehicles’ lithium ion batteries.
We would like to thank our three speakers for participating and sharing their thought-provoking insights with us. We would also like to thank the King’s Sustainability Team and KCLSU for their support in organizing our panel event. A big thank you also goes to our audience for being incredibly dynamic and engaged in the discussion. We look forward to welcoming you to King’s Think Tank events in the future!
This blog was written by Nicola Hogan, Sustainability Operations Manager at King’s.
Kings College London has been Fairtrade accredited since 2017.
In order to achieve the accreditation, King’s needs to demonstrate on-going commitment to the organisation in our sale of Fairtrade products and in our engagement with stakeholders. We’ve done this by organising events awhich support and promote Fairtrade and advertise the selection of Fairtrade products on sale across King’s campuses.
King’s support of ethical organisations is part of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
As we enter this ‘decade of action’, the ‘Ten Principles of Fairtrade’ ask not just for a fair price for workers, but also champions Health and Safety, Transparency and Accountability and Capacity Building. It also includes an anti-slavery principle where it protects against child and forced labour.
However, in recent years the ethical business market has become crowded as more and more sustainable and ethical labels are popping up. At King’s we support Fairtrade, as it helps to achieve the 17 SDG goals and especially speaks to SDG 5: Gender Equality through it’s support in empowerment of women.
In addition, research indicates that farmers often strive to be Fairtrade accredited for the sustainability of the land as oppose to purely economic reasons. For these reasons it’s important that King’s continue to be accredited with Fairtrade.
Simply look for the Fairtrade label on products such as coffee, chocolate or clothing.
If you’d like to know more about Fairtrade at King’s and perhaps embed Fairtrade in your teaching, research or departmental operations, please contact sustainability@KCL.ac.uk
This guest blog comes seventh in a series of blogs on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) courtesy of Onna Malou van den Broek, second year doctorate student at King’s in the European & International Studies Department. Onna’s doctorate project titled: ‘The Political Payoff of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): CSR as a Determinant for Lobbying Success’, which looks at the relationship between corporate sustainability and lobbying, holding a special focus on the SDGs.
“We need to help these poor countries develop, to create industries that are able to compete globally, and better their lives” – as spoken by a British diplomat at a conference I recently attended. Without going into the problematic post-colonial mindset, it also raises a fundamental economic question (1). Underdeveloped countries need to develop. However, the so-called developed states are destroying our world. What will happen if all countries reach this level of industrialization?
SDG 9: Innovation, industrialization and infrastructure
The starting point of this goal, just as we’ve discussed with goal 8, is that industries are the core drivers of the global development agenda (2). Reliable infrastructures and technological innovations are necessary to deliver the other goals, such as health care, sanitation and access to education. Some goals, for example, can be delivered through internet services. However, around 3.8 billion people, mainly from the least developed countries, still lack internet access. The growth of industries is closely tied to the global political economy. As a result of increased trade barriers and tariffs in 2018, global manufacturing and associated employment slowed down.
The Targets: Manufactory, mobility and research
This goal includes three broad issue areas which is reflected in the wide variety of indicators (3). Three indicators directly target the development of industries, aiming to stimulate inclusive industrialization; to provide access to financial credit for small and medium enterprises; and to make existing industries more sustainable in terms of clean and efficient resource-use. In addition, industry developments are heavily dependent upon innovation and, as such, the indicators aim to encourage industrial research and development through policies. Lastly, to include everyone in the process of industrialization, the indicators underline the importance of broad access to reliable infrastructure, such as all-season roads, energy-transmission or internet. Developed countries can support developing countries by providing access to novel information, finances and technology.
World’s system theory (Wallerstein)
 The central role of global political economy and trade has led to many critical scholars arguing the link between inequality and industrialization. One of the most influential is the world system theory, developed by the socialist Wallerstein in the late 20th century. This theory is influenced by the dependency theory and zooms in on the terms of trade (4). The main argument is that cheap labour and raw materials flow from low-income countries to high-income countries, who in turn, use these raw materials to manufacture goods which they sell for a much higher price back to low-income countries. This exploitative structure of trade and capitalism makes it difficult for low-income countries to escape.
The central role of global political economy and trade has led to many critical scholars arguing the link between inequality and industrialization. One of the most influential is the world system theory, developed by the socialist Wallerstein in the late 20th century. This theory is influenced by the dependency theory and zooms in on the terms of trade (4). The main argument is that cheap labour and raw materials flow from low-income countries to high-income countries, who in turn, use these raw materials to manufacture goods which they sell for a much higher price back to low-income countries. This exploitative structure of trade and capitalism makes it difficult for low-income countries to escape.
The Entrepreneurial State
Given that this is a government-led development Agenda, it is interesting that innovation is part of this goal. Some people have argued that innovation should be left to the dynamic entrepreneurs of the private sector instead of bureaucratic governments. In her book ‘the entrepreneurial state, Mariana Mazzucato refutes this argument and aims to debunk the public versus private sector myths. In her study, she finds that the private sector only finds the courage to invest after an entrepreneurial state has made the high-risk investments. For example, every technology that makes the iPhone so ‘smart’ was government funded. She criticises economic growth by showing a dysfunctional economic dynamic where the public sector socializes risks, while private sectors gets the rewards.
Resource-efficient infrastructures
Infrastructure developments, such as roads, buildings, energy and water infrastructure, are really resource intensive. They account for almost half of the global footprint. As such, resource efficiency of infrastructure can be a major driver of the transition to sustainable development. The UN Environment recently published a policy brief (6) in which they argue that our current project-by-project approach to infrastructure planning results in inefficient service delivery. System-level approaches, on the other hand, can increase the efficiency as they are better able to respond to user needs and capture positive industry spill-overs. This type of approach considers the economic, social and environmental impact of infrastructure systems, sectors, their location and relevant governance framework throughout the entire lifecycle, enabling industrial symbiosis and product circularity.
What can you do?
- Since this goal takes place on a systems-level, your first step is to inform yourself about issues such as global trade, international power imbalances and the grow-degrowth debate. There are plenty of resources. Books that I found useful are: ‘degrowth: a vocabulary for a new era’ and ‘a splendid exchange: how trade shaped the world’.
- Use your dissertation to contribute to knowledge around these topics. Talk to lectures about what research question might fit your specific programme and use your outcomes to start dialogues with different groups of people, such as policymakers, NGOs or firms.
- Due to the high level of abstractness, it is especially important to put pressure on your local, regional, national and international political representatives by tweeting, writing, voting, etc. to make sure they implement good policies.
References
(1) For a more elaborated discussion about economic growth, you can read the blog on SDG8 I wrote last month.
(2) Read more about why this goal matters: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/9.pdf
(3) Specific indicators, targets and progress can be found here: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdg9
(4) An easy and fun way of learning more about the system theory is through this video clip: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yRLd7xJNn14
(5) Buy the book at your local bookshop or watch the four things you need to know in 60 seconds: https://marianamazzucato.com/entrepreneurial-state/
(6) The UN policy brief can be found here: https://www.greengrowthknowledge.org/sites/default/files/downloads/resource/Policy%20Brief%20-%20Making%20Infrastructure%20Resource%20Efficient.pdf
This guest blog comes courtesy of Jessie Hardcastle, staff member working as the Fit for King’s Manager within the Estates & Facilities Department.
Jessie’s Vegan Story
When I joined King’s in June 2009 I quickly thought “what a wonderful place to work” – you know when you just find yourself looking forward to getting out of bed in the morning to see your colleagues? I knew this was my kind of place, filled with my kind of people.
10 years later in a very different job and working alongside completely different people I still think that. For lots of reasons. But certainly when Vision 2029 rolled out and the university announced that we are striving to make the world a better place all my personal values (which definitely also drive me at work) hummed happily.
Recently King’s has kept me humming happily even more than usual – because it doesn’t seem to matter which campus I’m on, I can find a vegan breakfast, vegan lunch and perhaps even more importantly – vegan cake for “elevensies”. I use to venture more onto the high street to find vegan options (there are plenty of options there too!) but frankly, the variety of options at King’s tends to be better.
I went vegan for a fairly common reason – I didn’t like the idea of killing an animal for a meal myself, and I didn’t want someone else to do it for me. And when I looked into it, other animal products were not separate to but part of that same industry.
This was a little over 18 years ago when I was still living in Auckland. Without wishing to sound like your plant-based-gran, I can’t help but tell you that “back in those days we didn’t have things nearly so easy.”
I remember one evening, not long after going vegan, I complained to my Mum the only thing I could eat in the fridge were three peppers. “At least there is a red, a green and a yellow one” she said!
Thankfully I enjoy a lot more variety than that now. And despite how that sounds, my family actually quickly became very supportive. I’ve also very rarely had any stigma from my friends and colleagues that wasn’t meant in good humour.
The biggest change in my life recently was giving birth to a baby girl in September 2018. I was secretly worried I might have a small baby that people would claim to be malnourished because of my vegan diet. Enter Charlotte Grace, weighing a whopping 9lb 14oz and quick to dispel that myth. Now a healthy sized toddler, she’s has a good appetite, definitely thriving and eating a wide variety of food. She shared some veggie sushi with me the other day, bravely trying new food without the bat of an eye. That might have been a different story if I’d includes the wasabi mind you.
Going vegan is so clearly linked with my other life choices, that how I spend my money, time and energy can help shape the world I want to live in. And for me, that includes working for an organisation that wants to make the world a better place.
This guest blog comes courtesy of Isabella Trujillo-Cortes, 3rd year Biomedical Engineering student at King’s who participated in the three-week micro-internship opportunity (organised by King’s Careers) with the King’s Sustainability Team in April 2019. This blog comes last in a series of three blog posts from Isabella.
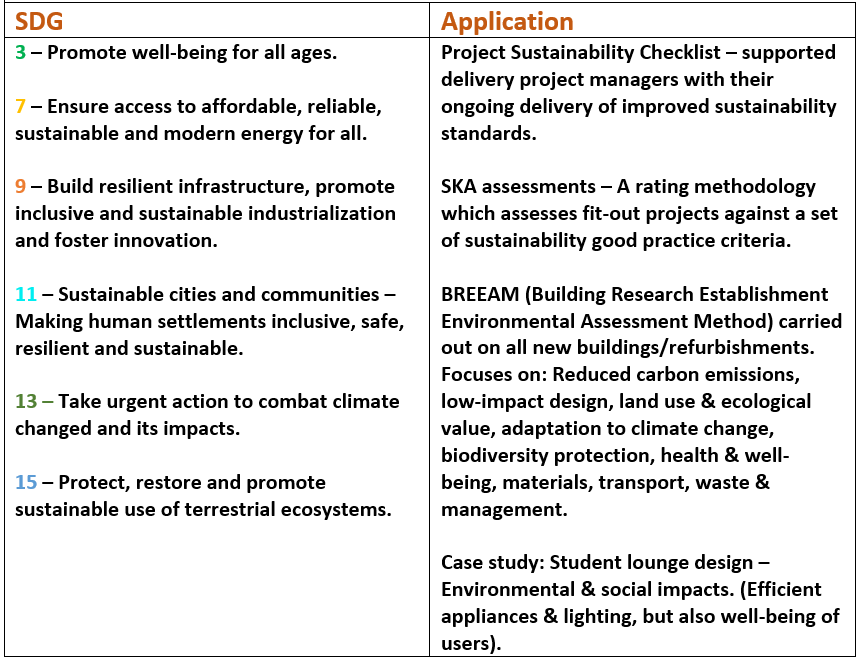
Sustainability in Estates & Facilities
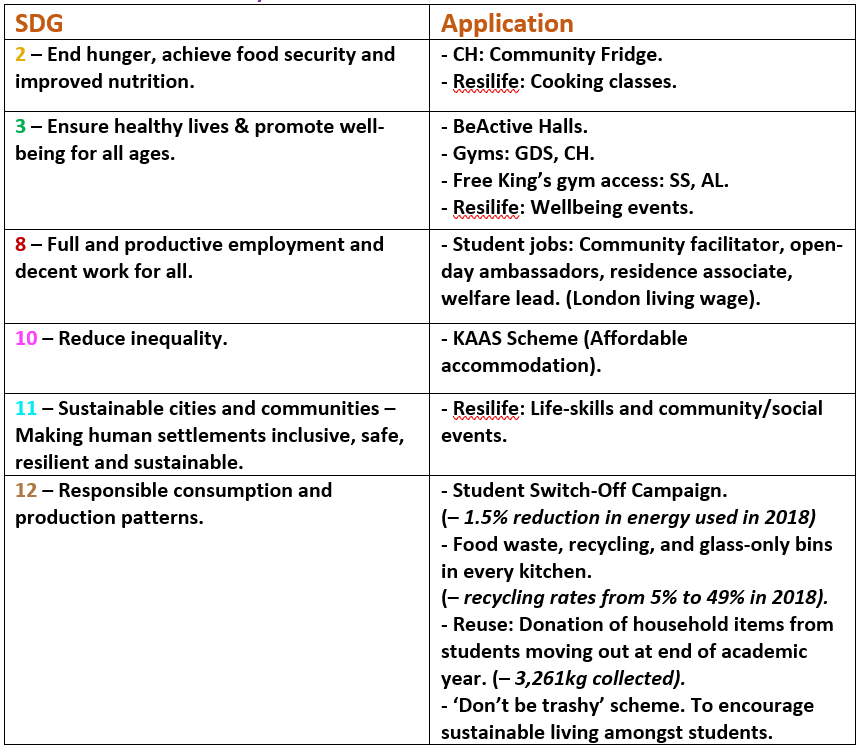
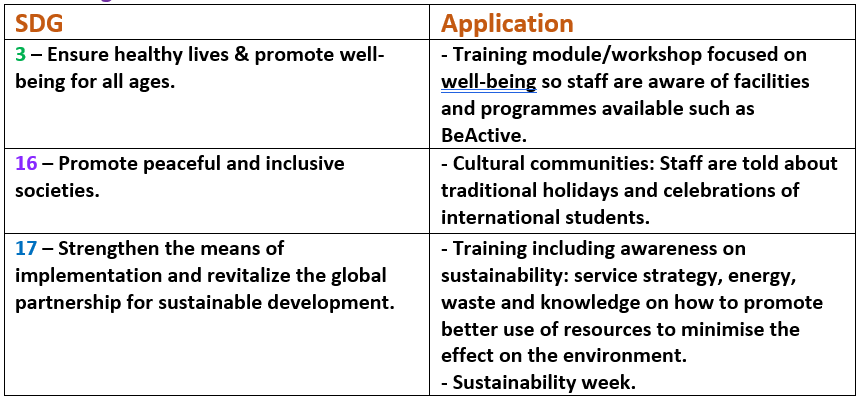
Student Accommodation / Residences
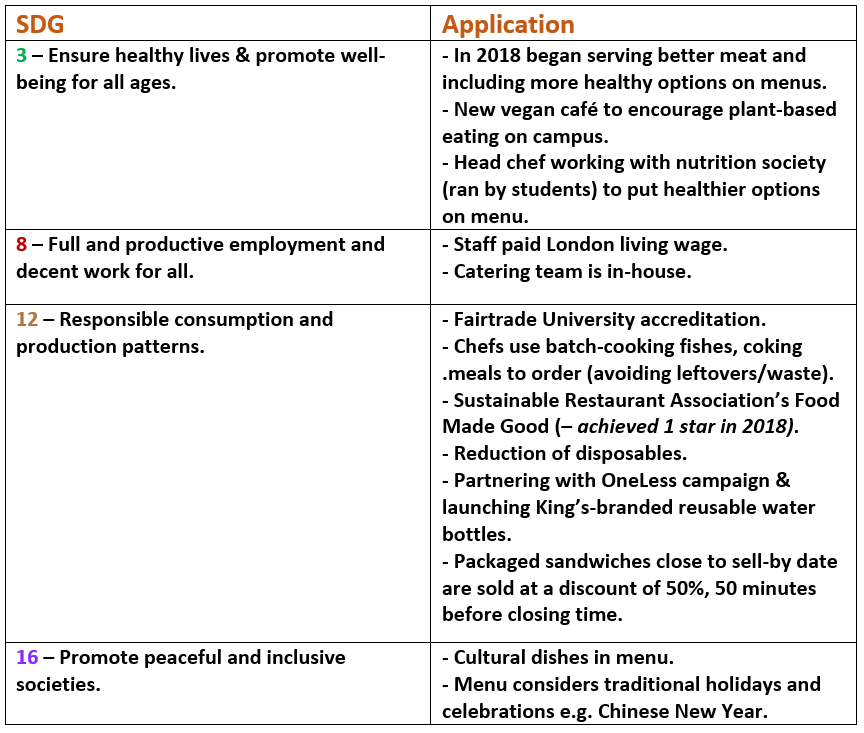
King’s Food
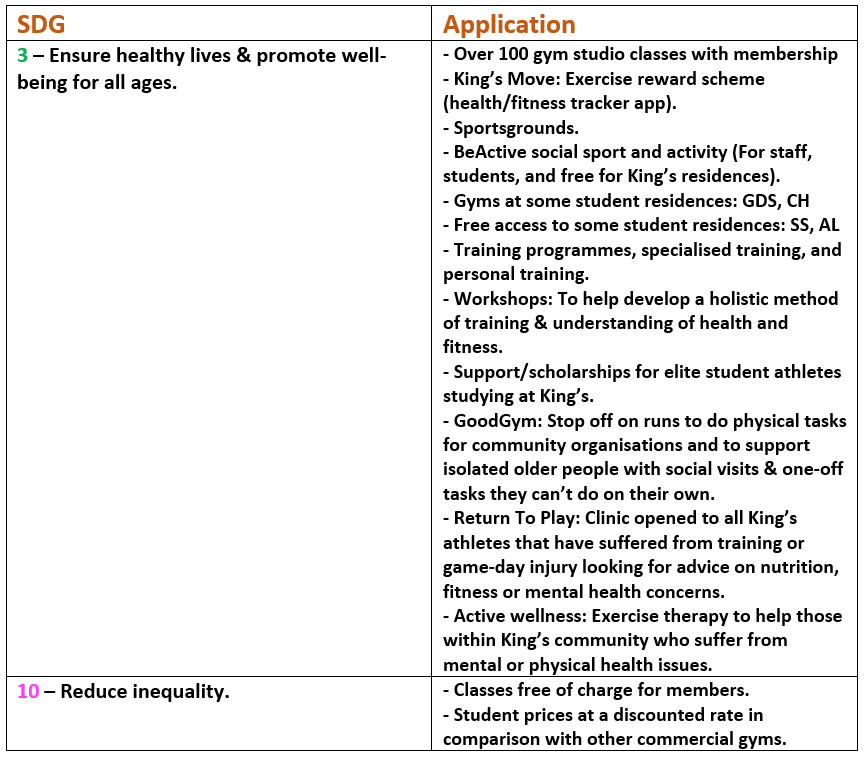
King’s Sport
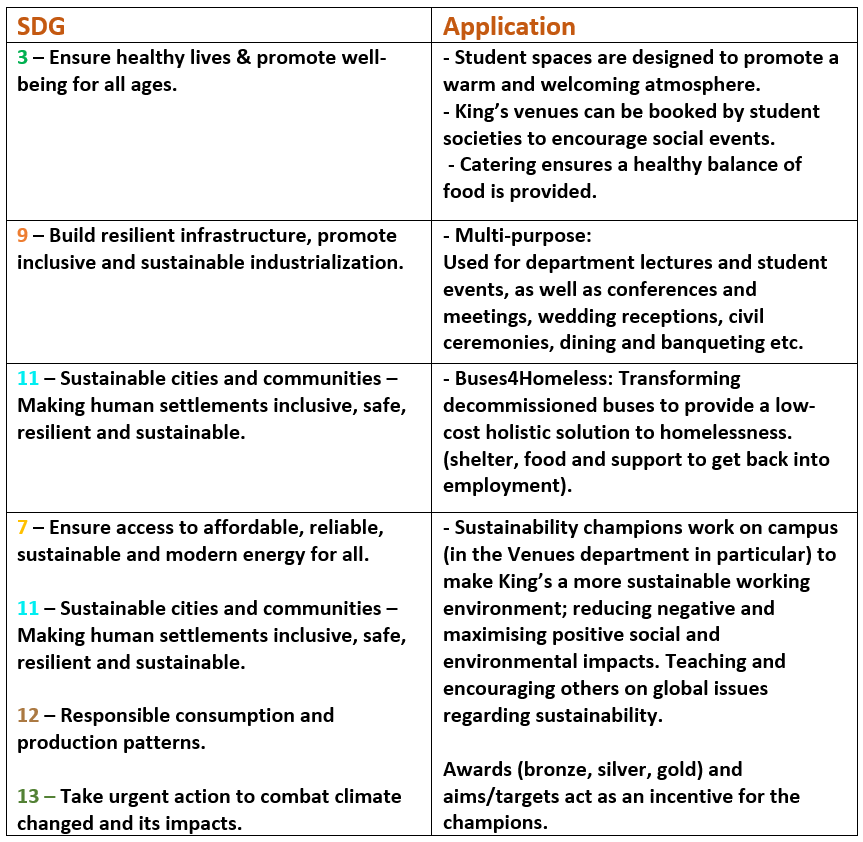
King’s Venues
Fit for King’s
Asset Improvement & Space planning
Evaluation
- The United Nations state that good health is essential to sustainable development, and thus, King’s highly encourages healthy living and well-being. SDG 3 is the most popular within the department and maps across almost every division.
- SDG 8 focuses on energy productivity. Given the number of computers, projectors and TVs across the university campuses it is vital that the Estates & Facilities department minimises the amount of energy consumed.
- Income equality affects staff and students as it may prevent them from pursuing opportunities. SDG 10 states empowering lower income earners is vital, and Kings are taking many approaches to work on this. In some areas, for example, the Estates & Facilities department gives discounted rates to those with lower income.
- An SDG also commonly shared across the department is SDG 11. To face the rapid growth of cities and increasing rural to urban migration, it is vital to focus on sustainable development. As Estates and Facilities manage the venues, residences and space planning in the university this SDG addresses this department most than the others at King’s.
- SDG 12 is also implemented in almost every division. Aside from meeting the social responsibility and service targets, King’s also focuses on environmental aspects. It is important that we reduce our ecological footprint by adjusting our consumption and production methods. This goal is being achieved in the way King’s manages the world’s shared natural resources and disposes of toxic waste and pollutants.
SDG 13 is also quite similar to 12. In managing our consumption and production methods, the human impact on climate change is reduced. - King’s is ranked as the world’s 14th most international university with over 40% of students being from outside the UK. The university focuses on establishing an inclusive community where students from abroad feel they are welcomed. This maps out SDG 16 which encourages peace and unity.
- SDG 17 explains that the SDGs can only be realized with strong partnership and cooperation. To achieve this on a global scale we must begin locally. The Estates & Facilities department does so by raising awareness of sustainability and service to staff and students.