Thais Russomano, MD, is a Senior Lecturer at the Centre of Human & Applied Physiological Sciences, part of the Faculty of Life Sciences & Medicine’s School of Basic & Medical Biosciences.
Thais Russomano, MD, is a Senior Lecturer at the Centre of Human & Applied Physiological Sciences, part of the Faculty of Life Sciences & Medicine’s School of Basic & Medical Biosciences.
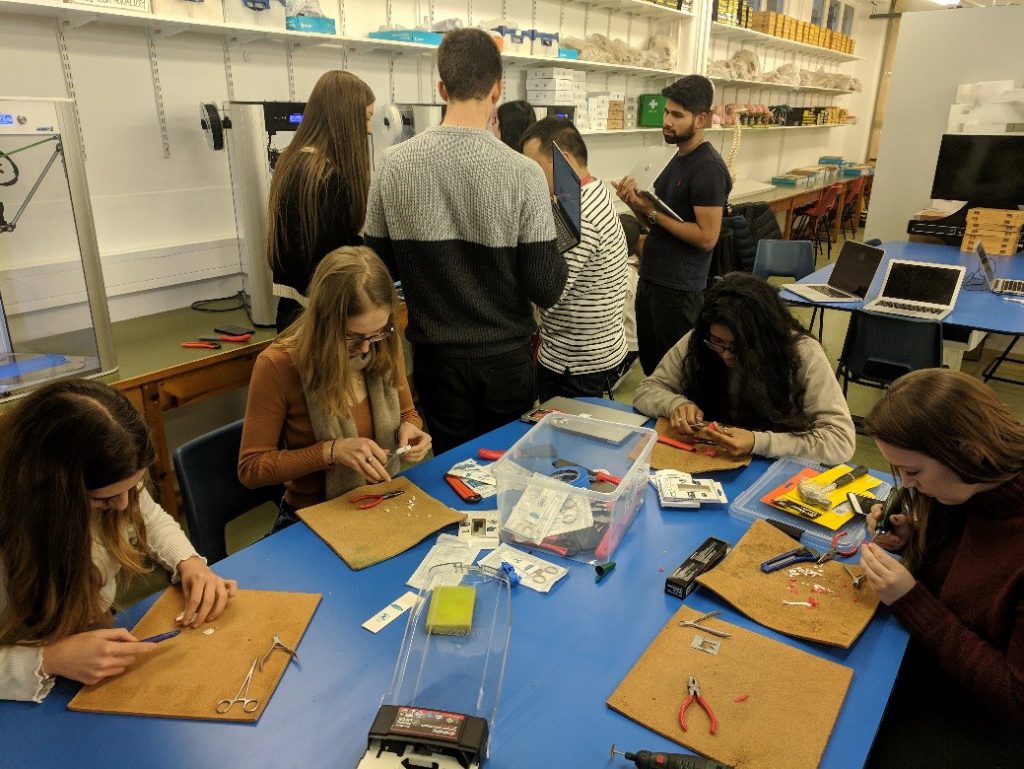
Thais teaches summer school students about body systems and how humans adapt when exposed to hostile environments.
If asked at the age of 16 what I wanted to be when I ‘grew up’, the answer university professor would never have crossed my mind. I knew what I wanted to be, it was simple – for as long as I could remember I dreamt of becoming an astronaut. This would be a difficult career path for anyone to follow, however, coming from a country (Brazil) that didn’t at that time even have a Space Agency made the task as difficult as climbing Mount Everest blindfolded! I wish at that stage of my life I’d had the opportunity to experience a course like the King’s Summer programme.
Exposure to material taught by an international professor in a ‘university-type’ form would certainly have given my confidence a boost and allayed many of the doubts I had about studying abroad and at a higher level. Nonetheless, I planned my journey, completing medicine in Brazil, then facing my fears and going oversees for a 2-year MSc in Aerospace Medicine in the US, and a PhD in Space Physiology at King’s College London, before working at the German Space Agency (DLR).
My academic career began at a university in Brazil, where I established the Microgravity Centre, a pioneering Space Life Sciences Research Centre, but my links with King’s always remained strong, and I eventually became the Deputy Course Director/Senior Lecturer of the Space Physiology & Health MSc course. Another constant in my life was dedicating spare time to teaching school-aged students about the life and works of astronauts during space missions.
Therefore, when asked to participate in teaching for the King’s College Summer Programmes, I was delighted to accept, as, from my own student experience, I knew the benefit this kind of interaction brings – I see it as a two-way win-win situation for both students and professors, both of whom encounter different learning styles and gain from an exchange of cultural values, which broadens perspectives and adds to personal and professional growth.
The design of the Summer Courses fosters this interaction of tutors/students and provides an enriching learning environment. Students gain a great insight into what life would be like studying at university level, and possibly experiencing for the first time a British way of delivering knowledge. This opportunity also gives a special experience to us as professors, entering a highly multicultural environment, bringing with it challenges as to how best to engage these young minds, but at the same time making the teaching-learning process more stimulating and special.
Given the short length of the courses, they can be no more than simply ‘taster’ experiences for both sides, however, the enthusiasm and curiosity of the students is evident from their willingness to participate in activities, and from their questions, which become more probing and frequent as the week progresses and confidence grows. And it is exactly this growth in confidence, this exposure to professors of a different culture, and this opportunity to mix with a different way of doings things that is the most invaluable lesson of the week for students, opening their eyes to potential new horizons.
Likewise, teaching pre-university students, and especially those from a culture for whom English is not their native-tongue, provides lecturers with a reminder that sometimes we must adapt our skills to better communicate the content of our classes, making the language we use more accessible, building on logical reasoning and employing good analogies that help in the understanding of more complex ideas. I am reminded that these skills are important within our practice at King’s, which is by its very nature, a very international university, with more than 40% of its student population drawn from 160 countries.
For me, the experience of teaching young students on King’s Summer Programmes is gratifying and enriching; something new to add to my lifelong learning portfolio. For the students, I hope they find their pre-university programmes inspiring and motivational experiences, bolstering their self-belief and turning the first page of their academic journey.