The King’s Doctoral Students’ Association (KDSA) is the recognised representative body of the Postgraduate Research Student community. It is an autonomous body within the KCLSU representative structure and drives for the changes that doctoral students want to see.
Aim & Mission
KDSA is independent of King’s and works with the university to drive the changes doctoral students want.
- Uphold, extend and defend the rights of doctoral/ postgraduate research students at King’s.
- Establish a Peer Support Network for both academic and non-academic issues.
- Promote student-led activity amongst new and existing PGR communities to build professional skills, share research ideas & network.
Watch the KDSA introductory video and meet the board members below:
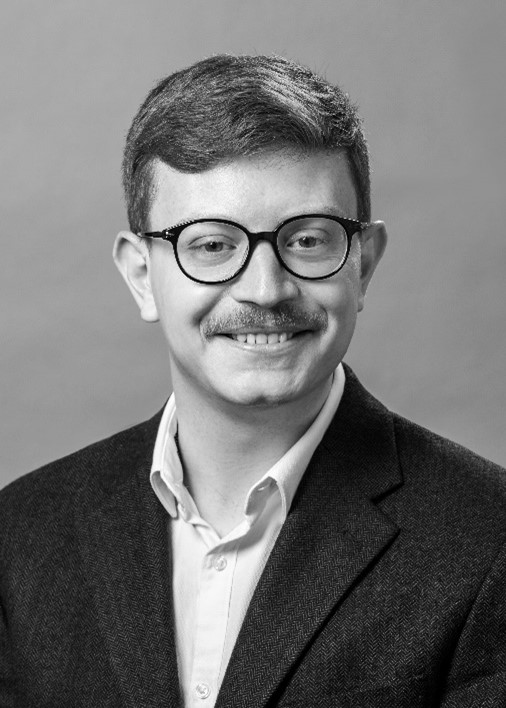
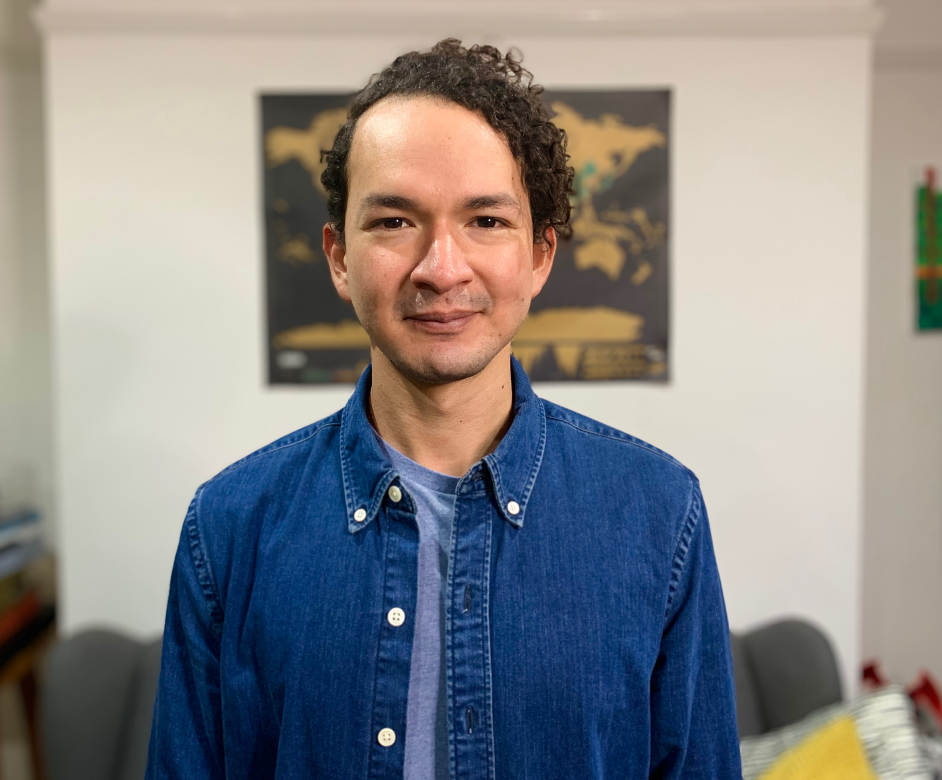
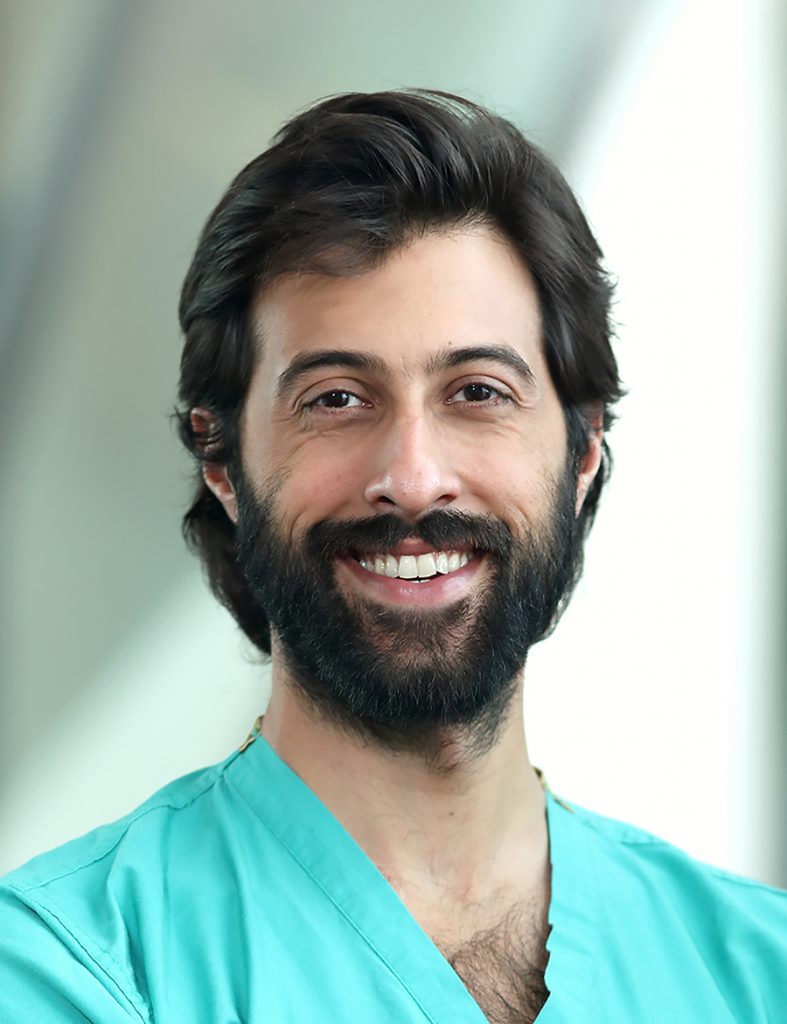
Dionysios Malas, President
 Dionysios graduated with an MEng Mechatronic Engineering degree from the University of Manchester in 2020. He realised what is the preferred professional career he would like to pursue from a young age and after a patellar dislocation for which, due to surgical error, he had to be operated on several times. The incident intrigued him to become a Medical Robotics researcher to help in the development of innovative solutions to precision surgical procedures.
Dionysios graduated with an MEng Mechatronic Engineering degree from the University of Manchester in 2020. He realised what is the preferred professional career he would like to pursue from a young age and after a patellar dislocation for which, due to surgical error, he had to be operated on several times. The incident intrigued him to become a Medical Robotics researcher to help in the development of innovative solutions to precision surgical procedures.
His research interest includes the lack of tactile feedback in medical robotics systems and tool, which is a widely cited disadvantage associated with robotics. Currently he is a PhD student trying to develop a novel technique to enable real-time force and shape sensing of an endoscopic tool called, MorphGI.
Check out Dio’s LinkedIn, Surgical & Interventional Engineering CDT
Mauro Bonavita, Vice President
Mauro is a second year Ph.D. student in International Relations, based at the King’s India Institute and War Studies. Mauro’s research focuses on Indian foreign and maritime policy in the Indo-Pacific region, as well as great power competition taking part in the Indo-Pacific. He obtained a Master’s degree in Geopolitics and Strategic Studies from University Carlos III of Madrid, and a Bachelor’s degree in Political Science from the University of Genova. He is currently affiliated with the Centre for Grand Strategy at King’s College London. In the KDSA board for the academic year 2021-2022, he is the Vice President.
Davide Ferrari, Secretary & Treasurer
I am Davide Ferrari, scientist, blogger, and learner.
In 2021 I started my PhD at King’s College London, at the King’s Centre for Doctoral Training in Data-Driven Health.
After a Master’s in Musical Arts and a Master’s in Computer Science, I decided to devote my strengths to medical application of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science.
Check out Davide’s YouTube, Instagram, LinkedIn, Twitter
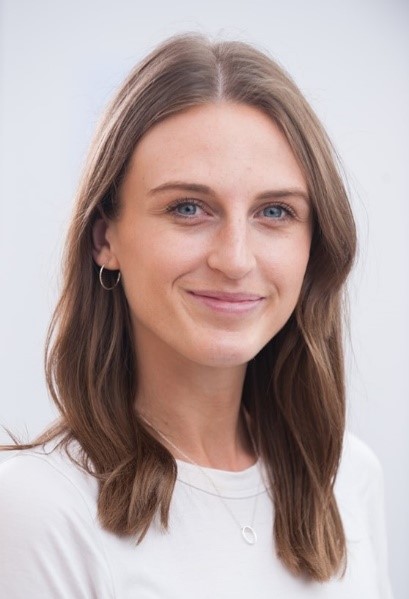
Katie White, Representative for the part-time PGR community
I am a 2nd year PhD student in the Department of Psychological Medicine at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience. My research explores how and why people engage with remote measurement technologies (wearables, smartphone apps) for symptom tracking in major depressive disorder. I am completing my PhD part-time whilst also working as a research assistant on the RADAR-CNS Public Private Partnership study. Before joining King’s, I completed a Psychology BSc at the University of Bath. I am thrilled to be the first part-time PhD rep on the KSDA board and look forward to ensuring that part-time students’ voices are heard and championed during their PGR journey.
Check out Katie’s LinkedIn, KCL Pure, Twitter
Roger Carles Fontana, Event Coordinator and Wellbeing Lead
 I am a second-year PhD student at King’s College London studying the role of miRNA present in extracellular vesicles in cancer metabolism at the Roger Williams Institute of Hepatology (School of Immunology and Microbial Sciences). My working PhD title is “ExomiR resetting of the energy profile in HCC via the mitochondrial proteome”. I am the KDSA Event Coordinator and Wellbeing Leader, from where I hope to implement measures aimed at improving PGR students wellbeing by addressing issues concerning burnout, work-life balance, PGR sense of community and student-supervisor relationships. Prior to my PhD, I conducted research projects in cancer and extracellular vesicles in the United States and the Netherlands in the context of his master’s degree in Biomedical Sciences, awarded with cum laude. I also worked as a research assistant at the Barcelona Biomedical Research Park, where my work focused on the potential adverse effects of ionising radiation from medical procedures.
I am a second-year PhD student at King’s College London studying the role of miRNA present in extracellular vesicles in cancer metabolism at the Roger Williams Institute of Hepatology (School of Immunology and Microbial Sciences). My working PhD title is “ExomiR resetting of the energy profile in HCC via the mitochondrial proteome”. I am the KDSA Event Coordinator and Wellbeing Leader, from where I hope to implement measures aimed at improving PGR students wellbeing by addressing issues concerning burnout, work-life balance, PGR sense of community and student-supervisor relationships. Prior to my PhD, I conducted research projects in cancer and extracellular vesicles in the United States and the Netherlands in the context of his master’s degree in Biomedical Sciences, awarded with cum laude. I also worked as a research assistant at the Barcelona Biomedical Research Park, where my work focused on the potential adverse effects of ionising radiation from medical procedures.
Check out Roger’s LinkedIn, Research Gate, Twitter
Chiara Mignani, Equality, Diversity and Inclusion Co-Lead
 I am a cultural manager and a Ph.D. candidate in lacemaking and Data Visualization. I am investigating the social and economic impact of cultural institutions within the urban environment. I use digital semantic mapping and analysis to understand and map urban dynamics. Particularly, my work focuses on the city of Venice and aims to contribute to the maintenance of the city as a center for artistic production and engagement.
I am a cultural manager and a Ph.D. candidate in lacemaking and Data Visualization. I am investigating the social and economic impact of cultural institutions within the urban environment. I use digital semantic mapping and analysis to understand and map urban dynamics. Particularly, my work focuses on the city of Venice and aims to contribute to the maintenance of the city as a center for artistic production and engagement.
Prior to my PhD I have worked as Marketing Manager in Istanbul and Venice, and helped start-ups in the field of urban development and sustainability to develop their marketing strategy.
I am Diversity and Inclusion co-lead and I want to contribute to design inclusive policies and work hard to demonstrate how much an inclusive approach can be a powerful asset for the university and its students and staff.
Check out Chiara’s LinkedIn, Twitter
Zeynep Sahin, Equality, Diversity and Inclusion Co-Lead
 Zeynep is the Diversity and Inclusion co-lead for KDSA. She is a first-year PhD candidate at the Department of Old Age Psychiatry where her work uses retinal imaging and artificial intelligence to detect and diagnose neurodegenerative diseases at the earliest point possible. Prior to joining KCL, Zeynep was a research fellow at the University of Cambridge.
Zeynep is the Diversity and Inclusion co-lead for KDSA. She is a first-year PhD candidate at the Department of Old Age Psychiatry where her work uses retinal imaging and artificial intelligence to detect and diagnose neurodegenerative diseases at the earliest point possible. Prior to joining KCL, Zeynep was a research fellow at the University of Cambridge.
Check out Zeynep’s Twitter.
Sangeeta Bhagawati, Social Media Coordinator
 Sangeeta joined King’s College as a PhD student in 2019. She is based in the Department of Comparative Literature and her research project is titled ‘Literature about and from the periphery: Identity and Belonging in Assam’.
Sangeeta joined King’s College as a PhD student in 2019. She is based in the Department of Comparative Literature and her research project is titled ‘Literature about and from the periphery: Identity and Belonging in Assam’.
Sangeeta has previously worked as a Communications Assistant at King’s Arts and Humanities Research Institute, and she is the current social media coordinator for King’s Doctoral Students’ Association.
Sangeeta holds a BA (Hons) in English Literature (Gauhati University, India), an MA (First Class) in English Literature (Gauhati University, India), an MPhil (First Class) in English Literature (Gauhati University, India) and an MA (First Class) in Postcolonial Studies (SOAS).
James Rowland, Representative for Faculty of Arts & Humanities
 I am a fourth-year PhD student in the Department of History at King’s College London. My research utilises contemporary newspapers and periodicals, parliamentary debates, works of political philosophy and travel literature to explore the influence of America on nineteenth-century British political reform debates leading up to the Second Reform Act. Prior to my PhD, I was a master’s student at King’s where I completed my thesis examining the impact of the American Civil War on the British Press. I am the representative for the Faculty of Arts & Humanities on the KDSA and look forward to working with the board to promote student welfare and strengthen the research community this year.
I am a fourth-year PhD student in the Department of History at King’s College London. My research utilises contemporary newspapers and periodicals, parliamentary debates, works of political philosophy and travel literature to explore the influence of America on nineteenth-century British political reform debates leading up to the Second Reform Act. Prior to my PhD, I was a master’s student at King’s where I completed my thesis examining the impact of the American Civil War on the British Press. I am the representative for the Faculty of Arts & Humanities on the KDSA and look forward to working with the board to promote student welfare and strengthen the research community this year.
Check out James’ LinkedIn, KCL Pure, Twitter
Natalie Sanford, Representative for Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing, Midwifery & Palliative Care
 Natalie is a third-year PhD student at King’s College London studying resilient healthcare and interprofessional teamwork. She is the KDSA representative for the Florence Nightingale faculty of Nursing, Midwifery, and Palliative Care, where she also serves as the Research Executive PhD representative, chairs the faculty Journal Club, and teaches as a GTA. Outside of her faculty, Natalie is involved with a number of projects through King’s Centre for Team Based Practice, including the Simulated Home Environment project, the When Harm Happens pilot, and the implementation of Student Schwartz Rounds. She also works with King’s Academic Skills for Learning as an Academic Skills Tutor. Natalie was a 2021 KCLSU Laurel Award Recipient and was also shortlisted for 2021 Student Representative of the Year. Prior to her PhD, Natalie worked clinically in the U.S. with internal medicine and cardiology patients and taught medical-surgical and high-acuity nursing at the University of Maine. She was an original participant in the development and trial of the Interprofessional Partnership to Advance Care and Education model in collaboration with Maine Medical Center, Tufts University School of Medicine, and the ACGME. She completed her master’s degree at the University of Edinburgh in 2016. Her working PhD thesis title is: “Resilience and Adaptive Capacity in Hospital Teams in England.” In 2021, she presented her preliminary PhD findings at multiple international conferences, where she won an award for Best Paper (EHF 2021) and was selected as an Emerging Talent in Resilience Engineering (NDM & REA 2021).
Natalie is a third-year PhD student at King’s College London studying resilient healthcare and interprofessional teamwork. She is the KDSA representative for the Florence Nightingale faculty of Nursing, Midwifery, and Palliative Care, where she also serves as the Research Executive PhD representative, chairs the faculty Journal Club, and teaches as a GTA. Outside of her faculty, Natalie is involved with a number of projects through King’s Centre for Team Based Practice, including the Simulated Home Environment project, the When Harm Happens pilot, and the implementation of Student Schwartz Rounds. She also works with King’s Academic Skills for Learning as an Academic Skills Tutor. Natalie was a 2021 KCLSU Laurel Award Recipient and was also shortlisted for 2021 Student Representative of the Year. Prior to her PhD, Natalie worked clinically in the U.S. with internal medicine and cardiology patients and taught medical-surgical and high-acuity nursing at the University of Maine. She was an original participant in the development and trial of the Interprofessional Partnership to Advance Care and Education model in collaboration with Maine Medical Center, Tufts University School of Medicine, and the ACGME. She completed her master’s degree at the University of Edinburgh in 2016. Her working PhD thesis title is: “Resilience and Adaptive Capacity in Hospital Teams in England.” In 2021, she presented her preliminary PhD findings at multiple international conferences, where she won an award for Best Paper (EHF 2021) and was selected as an Emerging Talent in Resilience Engineering (NDM & REA 2021).
Check out Natalie’s LinkedIn, Research Gate, Twitter
Sinuhé Perea, Representative for Faculty of Natural & Mathematical Sciences
 Hello there! I’m a PhD student in the Photonics and Nanotechnology Group, literally trying to see (with light) what is hidden. I like to solve problems, but since I rarely find any solution, preferring to learn and ask. I graduated in Physics and in Mathematics at University of Oviedo (Spain) where I was also a Computational Assistant and participated in European Exposcience and being awarded as best young researcher for CEULAJ & ICMAT (CSIC). Currently, I am GTA in the Physics Department while researching in near-field and topological photonics systems, algebraic Number Theory (OPN) and skyrmions.
Hello there! I’m a PhD student in the Photonics and Nanotechnology Group, literally trying to see (with light) what is hidden. I like to solve problems, but since I rarely find any solution, preferring to learn and ask. I graduated in Physics and in Mathematics at University of Oviedo (Spain) where I was also a Computational Assistant and participated in European Exposcience and being awarded as best young researcher for CEULAJ & ICMAT (CSIC). Currently, I am GTA in the Physics Department while researching in near-field and topological photonics systems, algebraic Number Theory (OPN) and skyrmions.
And remember, even primes are odd.
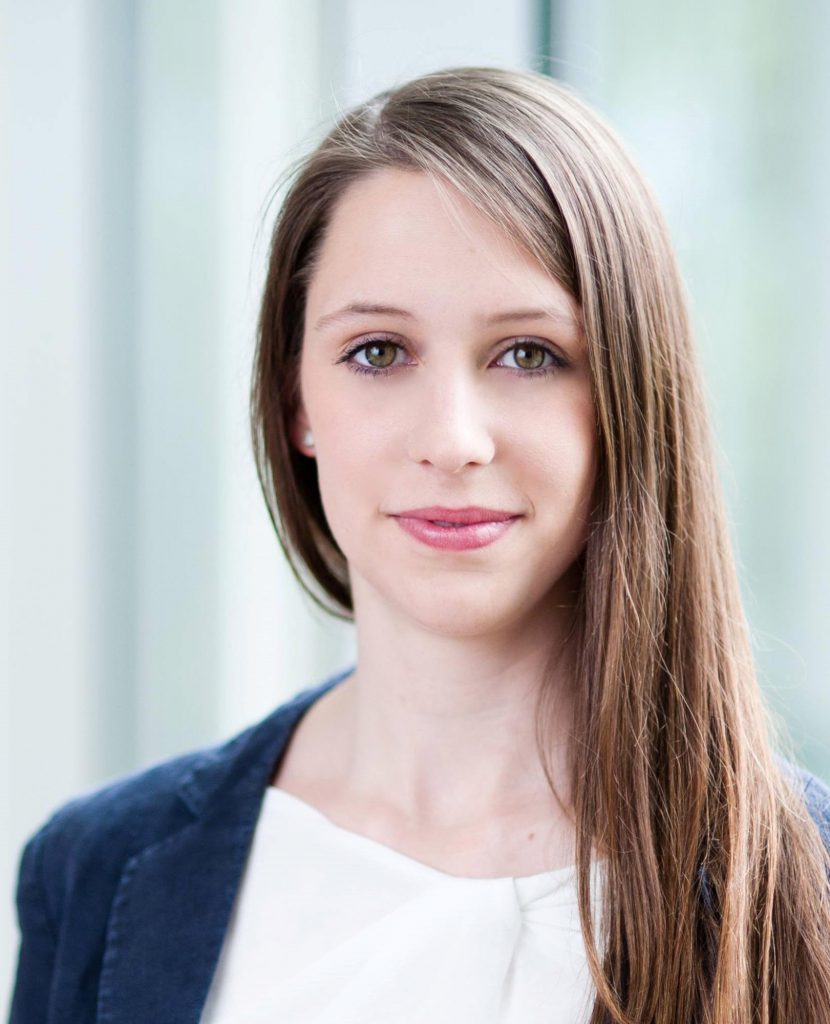
Lina Kramer, Representative for Faculty of Social Science & Public Policy
Lina is a second-year Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Political Economy based in the School of Politics and Economics. In addition, she is a recipient of the London Interdisciplinary Social Science Doctoral Training Partnership (LISS-DTP) studentship award which is funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC).
Lina’s research focuses on how AI can be used to design and improve tax policy. For this, she developed the AI Government, a deep reinforcement learning framework that allows her to run dynamic simulations and improve political and economic modelling.
Next to her PhD, Lina is the KDSA representative for the Faculty of Social Sciences and Public Policy (SSPP) and she is committed to enhancing the PGR student experience in SSPP. She is working closely with the Associate Dean for Doctoral Studies to ensure effective representation within the faculty and to strengthen the PGR community across the faculty.
Prior to her PhD, Lina worked for several years as a consultant on promoting the digitalisation of the German government and public sector. She further holds an MSc. in Economics from the University of Cologne and a BA. in Public Management and Governance from Zeppelin University.
Check out Lina’s LinkedIn.
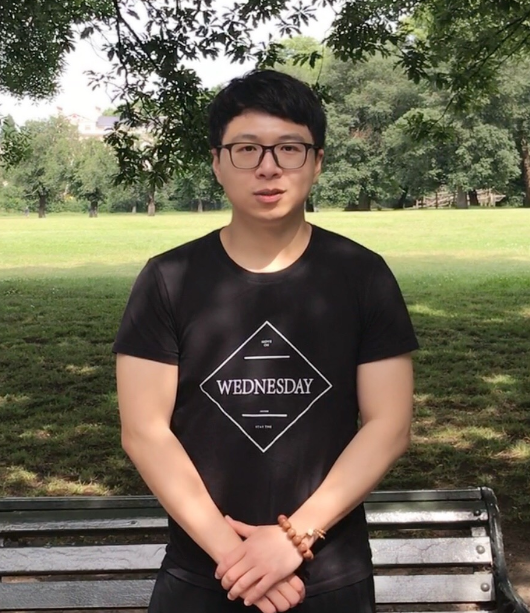
Mikel De Iturrate Reyzabal, Representative for Faculty of Life Sciences & Medicine
 I am a 2nd year PhD student in the School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences in the Department of Surgical & Interventional Engineering. My research analyses different ways of combining visual and haptic information to create a reliable low-latency data transmission using mobile networks for telesurgery. My focus now is on the use of GANs and other Deep Learning methods to compress the data and reconstruct it using the less amount of information possible, ensuring maximum performance at the same time. Before joining the PhD program at King’s, I studied my BSc in Biomedical Engineering in Universidad Carlos III in Madrid and the MSc in Healthcare Technologies here at King’s. I am thrilled to be the representative of the FoLSM on the KDSA board and look forward to helping every faculty PhD student.
I am a 2nd year PhD student in the School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences in the Department of Surgical & Interventional Engineering. My research analyses different ways of combining visual and haptic information to create a reliable low-latency data transmission using mobile networks for telesurgery. My focus now is on the use of GANs and other Deep Learning methods to compress the data and reconstruct it using the less amount of information possible, ensuring maximum performance at the same time. Before joining the PhD program at King’s, I studied my BSc in Biomedical Engineering in Universidad Carlos III in Madrid and the MSc in Healthcare Technologies here at King’s. I am thrilled to be the representative of the FoLSM on the KDSA board and look forward to helping every faculty PhD student.
Check out Mikel’s Linkedin, SIE Bio
Juliette Giacobbe, Representative for Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience
 Juliette is a 2nd-year PhD student at King’s College London. Her project is part of the H2020 EarlyCause project and focusses on the interactions between inflammation, stress, and hippocampal neurogenesis as pathophysiological mechanisms of depression. She is the KDSA representative for the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience. She completed a BSc in Psychology and Education at the University of Mons, Belgium, and a MSc in Cognitive and Clinical Neuroscience specialised in Fundamental Neuroscience at Maastricht University, the Netherlands.
Juliette is a 2nd-year PhD student at King’s College London. Her project is part of the H2020 EarlyCause project and focusses on the interactions between inflammation, stress, and hippocampal neurogenesis as pathophysiological mechanisms of depression. She is the KDSA representative for the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience. She completed a BSc in Psychology and Education at the University of Mons, Belgium, and a MSc in Cognitive and Clinical Neuroscience specialised in Fundamental Neuroscience at Maastricht University, the Netherlands.
Check out Juliette’s Twitter.
KDSA represents all postgraduate research students at King’s, and they are keen to hear from you! If you’ve got feedback to share or would like to find out about PGR events, get in touch via kdsa@kclsu.org, Twitter, or Instagram.