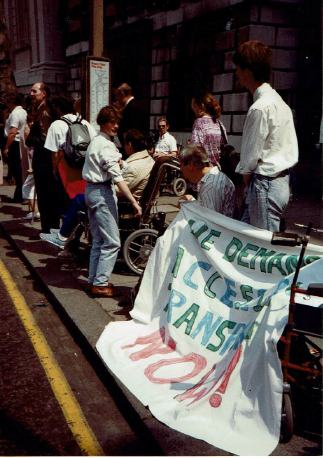This week, we share a blog from Savitri Hensman, Patient and Public Involvement Coordinator for Applied Research Collaboration (ARC) South London, based at IoPPN, which details a look back at the Campaign for Accessible Transport protests in London in the 90s. Thanks to Ruth Bashall for images.
‘We will ride’: making transport accessible
Getting to King’s College London, and around our city, is easier for many disabled people than it would have been a few decades ago. Public transport is far from fully accessible, especially the underground. The pandemic has added to problems. Yet much has changed, thanks largely to direct action by disabled campaigners.
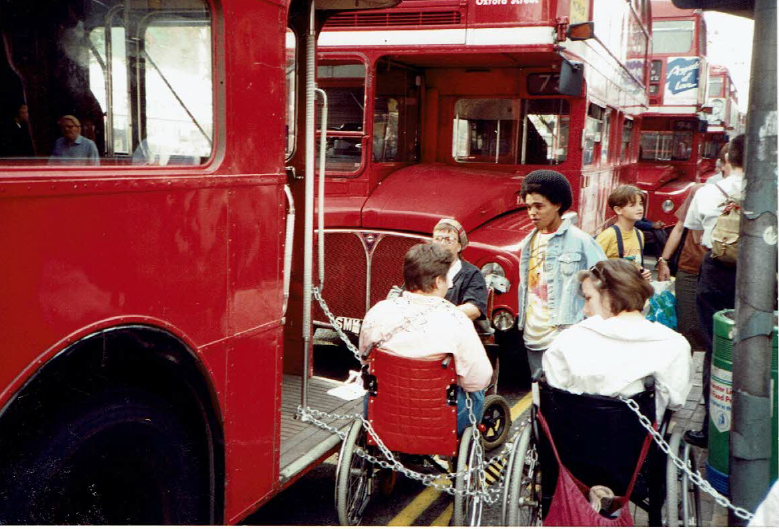
Thirty years ago, buses were generally impossible to use if one was unable to climb on board and were without written and audio announcements of stops. Even the limited access to the tube which now exists was not in place. Though members of the public, many disabled people could not get around on what was meant to be public transport. Calls for change were largely disregarded. But in 1990, the issue became hard to ignore, as protests brought traffic in parts of central London to a halt!
The Campaign for Accessible Transport (CAT) protested in high profile locations such as Oxford Street, for instance halting a bus as a wheelchair-user symbolically tried to get on. They explained to impatient passengers that, while their journeys were delayed, some people had been waiting for years to get to their destinations.
Activities were carefully organised, with plenty of photo opportunities for the media. Some protestors chained themselves to buses. A number of people were arrested; being willing to take this risk often involved a fair deal of courage, especially since police tended to have no training in how to move disabled people safely and getting into police stations and courts often meant being carried up flights of steps.
I was young and non-disabled back in those days. But friends who were involved in organising the events roped me in to be present as one of the legal observers. I was not part of the protests but was one of those who observed, kept note of who got arrested and police behaviour and, in general, helped to protect the rights of protestors. I had no legal training but I did have experience at anti-racist demonstrations, which offered useful opportunities to practice staying calm amidst often violent chaos. So on perhaps a couple of occasions, I showed up, looked on and kept jotting, on the sidelines of the action.
Singing was often a feature, including a song by an American activist, ‘We will ride’, which was adapted to the UK context.
These protests contributed to a broader shift in how disabled people were viewed in Britain, as those previously seen as helpless took bold action (though there is still a long way to go in tackling negative and disempowering images). In other ways too, disability rights activists – some of whom involved in diverse social movements for justice – were changing attitudes and practices.
Change did not happen immediately. But after CAT came DAN (Direct Action Network), with some overlap in membership. Newsworthy events happened in London and elsewhere, drawing attention to injustice in transport and other areas of life.
In 1995 a Disability Discrimination Act was passed, though tackling lack of access in transport through the law was a slow process. However some transport authorities were improving access; it was clear that disabled potential users were not willing to let the issue be forgotten. From 2000, the new Mayor of London introduced what was, for a while, probably the largest accessible low floor bus fleet in the world. Changes were also introduced in the underground and overground train network, though a new leadership did not keep up the momentum. Nevertheless the improvements had major effects on people’s ability to study, work or volunteer and be part of the community.
Making change happen often involves much lobbying and negotiation. But sometimes direct action may be needed, as happened so memorably all those years ago.