Emma Warnock-Parkes, Clinical Psychologist and exhausted mum of 2, shares 5 strategies for overcoming parental guilt.

Emma and her children smiling and laughing
I’m sitting in a lunchtime zoom meeting of fellow parents working at my university. The topic of discussion is how the pandemic has impacted on us. I’ve never met any of these people before but looking around I know we have one thing in common: we are all knackered. Many of us sit with a child on our lap or one repeatedly appearing in the background requesting more snacks. We simultaneously shovel down some lunch and keep an eye on our emails. As I half listen (a skill many of us have acquired thanks to COVID), I’m struck by the fact that in addition to all being exhausted and desperately needing a haircut, we are plagued with a common problem: guilt.
‘I’m not spending enough time with my kids’; ‘I feel bad they are stuck with me and cannot see their friends’; ‘He should have had a better birthday’; ‘I’ve given them too much chocolate’; ‘they are on screens far too much’, ‘I’ve shouted’, ‘I’ve sworn’, ‘I’m irritable with them’, ‘the house is constantly a mess’, ‘I’m not helping them enough with their school work’; ‘they are falling behind’. The list goes on.
I listen to other mums fighting back their tears as they beat themselves up over what has undoubtedly been the most difficult year of our lives. I’m suddenly overwhelmed with sadness and deep compassion for these amazing women, and for myself. This last year parents have faced unprecedent challenges. We have managed the anxiety and uncertainty of a global pandemic, alongside performing an impossible juggling act that no generation of parents has faced before. We have done all this while adapting to remote working, without our usual social supports, while being stuck inside our homes in an unrecognisable world. Many of us have had to worry about job or financial security, had friends and family who are struggling, coped with illness and loss. So why are we all being so hard on ourselves?
Given what a common experience it is, there is surprisingly little research on parental guilt.
Some psychologists argue that women feel more guilt than men, and that maternal guilt has an evolutionary basis motivating us to provide care (Rotkirch & Janhunen, 2009). One would hope this would change as parental roles become more shared. That said, I just asked my husband what he has felt most guilty about during the pandemic: he has eaten too much ice cream and not learnt enough Italian apparently. As this is a sample of one, and I happen to know Dads who have struggled with COVID parenting guilt, I’ll say no more.
As I listened to other parents talking, it struck me that as a psychologist and CBT (cognitive behavioural therapy) therapist I know quite a bit about helping people overcome guilt. Yet, like many good psychologists, I’m terrible at taking my own advice. I vowed that later that day I would get out the chocolate biscuits, put on yet another episode of Paw Patrol and give my pangs of guilt a self-therapy session. Here is what I found:
5 CBT tips you may find helpful for addressing COVID parenting guilt:
1) Spot your guilty thoughts.
Guilty feelings are driven by guilty thoughts, so spotting what you are feeling guilty about is the first step to overcoming it. Guilt arises from the perception that we have done something wrong or harmful to another: “should” thoughts. “I should be spending more time home schooling my children”, “I shouldn’t have got so angry” etc. These thoughts leads to feelings of guilt, and at times anxiety or low mood. This can understandably impact on what we do. We might dwell on our guilty thoughts or withdraw from others. This can become a vicious cycle, leading to more negative thinking and guilt: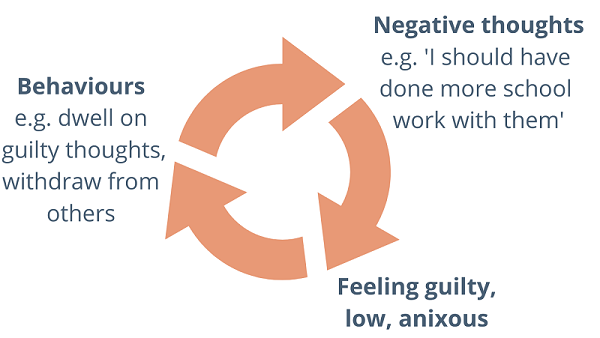
If you feel parental guilt about many things since COVID began, try to spot the thoughts that
makes you feel most guilty. For me this is not spending enough time with my kids.
2) Are you as responsible as you feel?
Feeling guilty does not mean that we are guilty, it may mean that we are taking on too much responsibility. A helpful CBT technique here is drawing out a responsibility pie chart. It can help you to see that there might be other factors that have some responsibility. This is done in 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Start by writing down how responsible you feel. For me, as Netflix helpfully asks whether my children are still watching Paw Patrol, I write, ‘I feel 100% responsible for not spending enough time with my kids during the pandemic’.
Step 2: Write a list of all the other factors that can take some responsibility. Here I write down: the COVID virus; the government for poor outbreak management leading to childcare closure; people who did not follow guidelines early on; my work; my husband; myself.
Step 3: Allocate percentages of the pie to each thing on your list (make it add up to 100%). Give a percentage to all the other things first, ending with yourself. Then draw out the pie chart. This is what I ended up with:
My Responsibility Pie Chart:
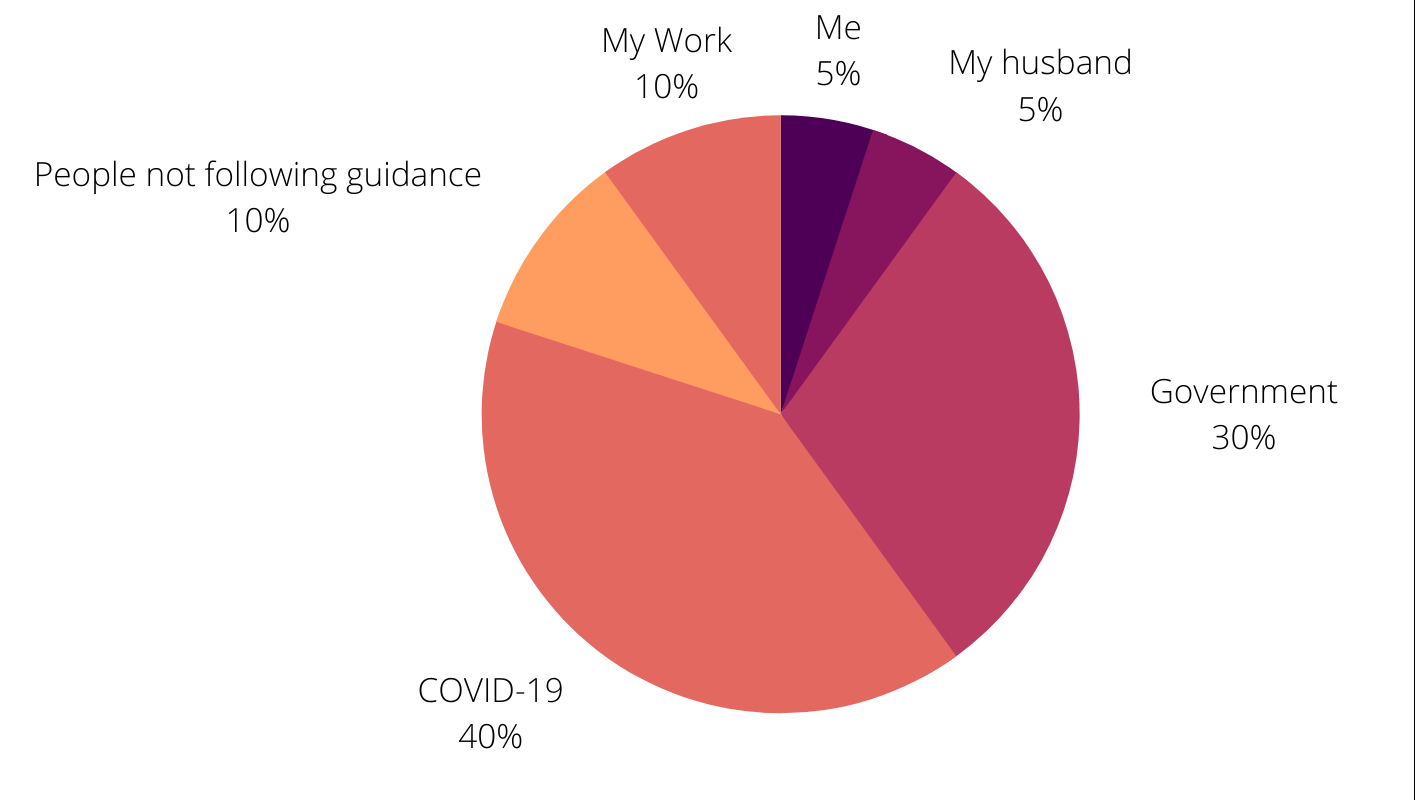
Drawing it out is a powerful reminder that despite feeling 100% responsible, we really cannot blame ourselves for a global pandemic and the impact it has had on our lives.
3) Focus on what you have done, not what you haven’t.
The pie chart helped, but I still feel some guilt. Guilt is often maintained by discounting what we have done, and instead focusing on what we have not. I spend a few moments writing down the things I have done for my children during the pandemic. I find this hard, so ask my husband to help. I also look back through the photos on my phone for the past year. This surprises me. I half expect to see nothing but photos of my children screaming through my zoom meetings as I throw snacks in their general direction. What I see instead is smiling faces in the garden, happy walks in the park, a couple of outdoor meet-ups with friends and family last summer, even a few shots of them eating fruit, instead of chocolate. All of these memories have been totally blocked by my feelings of guilt.
What strikes me is I how much I have done this last year to get us through. If I had time to frame or make a collage of these photos I would. I clearly don’t (cue more guilty thoughts). Instead, as a reminder of what I have done, I save one of us all smiling as my phone screensaver. It is an exercise I thoroughly recommend you try.

4) This year has been hard enough, so do what’s helpful.
Self-criticism and guilt go hand in hand and may have become a bit of a habit. It can help to explore what impact this is having on you and your family. Ask yourself:
a)Is being hard on myself helping us at all? For me, the answer is no.
b)Are there any disadvantages? For me, it makes me feel rubbish and much more in my own head, which in turn makes it harder to have fun with the kids.
If beating ourselves up is not helping us, or our children, it is probably a good idea to try to notice when dwelling on it, and to let it go. For me this includes dropping my standards. The kids won’t be getting any home-made hummus this year, and that’s ok (to be honest they only did once before COVID and, on account of it tasting like Polyfilla, nobody ate it anyway). I realise comparing myself unfairly on social media has not been helping. An Instagram photo only shows a one second window into the lives of others. You may see little Jessica eating a rainbow food bowl or practicing her phonics, but what you don’t see is the tantrum and screen time that come after. I decide to unfollow all the mummy food accounts on Instagram that tend to make me feel bad about myself. Quite frankly, if any of us manage to throw the occasional bit of broccoli in with the fish fingers this year, we are winning.
“Try not to compare yourself to other parents on social media.”
5) Be kind to yourself – What would you tell any other parent?
Thinking of the compassion I felt upon hearing my colleagues’ struggles, I remember how key it is to tune into kindness for yourself when struggling with guilt.What would we say to any other parent who has gone through/is still going through what we have? I spend a moment thinking of a close friend of mine who has had a hard year juggling work and kids. I first imagine what I would say to her. When I tune into my feelings of compassion, I then start writing a note to myself:
‘Dear Emma, give yourself a break! You have done the best you possibly could in the hardest year of your life. You’ve juggled full-time work and childcare for two children during a global pandemic. All while getting used to working at home, away from family and friends, with little sleep and no break. You deserve a medal rather than being so hard on yourself. Extra TV and snacks is essential COVID survival. You are doing a great job, even if you don’t feel like it. Be kind to yourself.’
Writing a compassionate message to yourself and reading it back may feel like a strange thing to do, but I wholeheartedly recommend trying it. Once you have, try to plan in a regular small act of self-kindness. I make a plan to take a proper lunch break away from the screen each day that week and read a little of my book (and when I managed it, it felt amazing). Our children can only benefit from treating ourselves a little better.
Feeling a little lighter, I close the laptop and turn off Paw Patrol. Once the whinging about the TV going off has stopped and I have mediated another row over Lego, my eldest son digs his elbow into my tummy, “squidgy mummy” he reminds me. He spots the exasperated look on my face and corrects himself: “you are the best mummy” he says.
For once I decide to let myself believe him. And you know what? The rest of the afternoon felt a little better for it.
If you are struggling with excessive feelings of low mood or anxiety, do reach out for help. Many employers, including my own university, offer psychological support through employee assistance programmes. There are helpful resources, including information on accessing talking therapies, on the Every Mind Matters NHS page.
NEST is our dedicated staff network for supporting parents and carers at King’s. they provide support to staff with parental and/or caring responsibilities through a range of events, an online community, and by offering guidance and representation at a strategic and policy level. You can find our more about NEST here.




